A homeowner needs to understand some of the differences between lambda values,
U values, and R values, when referring to material performance.
This is when constructing an extension or modifying his property or building a new home.
This relates to the SAP ratings you aim to obtain,
on your new build property or towards meeting the requirements of your building regulations on any building.
Lamabda value definition
The lambda value is a “K” value, and it measures the thermal conductivity of the product in units of W/Mk.
And good insulation of the lambda value will be as low as possible, to reduce heat loss.
For example, we have a lambda value for each lower lambda product,
which is 0.019 W/mK across all thicknesses.

Define the value of R
The R value measures the thermal resistance of a product in units of m²K/W.
You can find out how resistant a material is to heat transfer at a given thickness,
by dividing the material’s thickness (in metres) by its lambda value.
The better insulation will have a high R-value and a lower thickness,
indicating that it is just as good at reducing heat loss as its thicker counterparts.
Define the value of U
The value of U is the sum of the thermal resistances of the layers that make up a complete building element.
For example, ceiling, wall or floor, it also includes adjustments for any fasteners or air gaps.
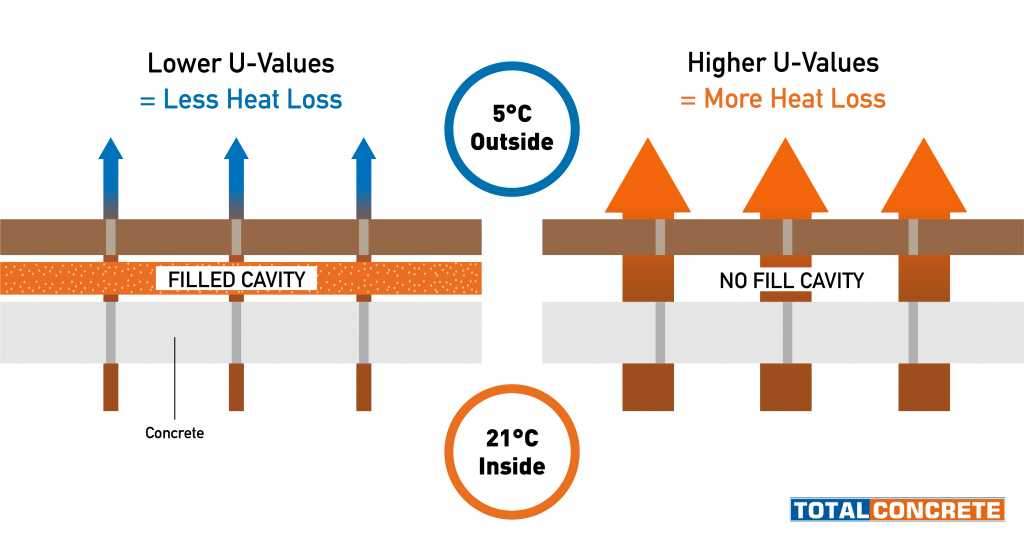
The value of U, in units of W/m²K, shows the ability of an element to transfer heat from a warm to a cold place in the building.
And vice versa, the lower the value of U, the better insulated the building element.
The U-value of a building element is very important as there are certain standards that must be reached as per building regulations/standards.
How are U-values calculated?
Most materials have known values by which heat is transmitted through them under specific conditions.
These values are known as k-values - a measure of the thermal conductivity, in any element of the building (such as a wall, floor, or roof).
The K values for each layer of material are divided by the thickness of that material,
to get the R-value for that layer or the thermal resistance.
The total resistance of almost the entire section of the wall is found when all values of R are added together.
The surface air resistance of the inner and outer face, and any fixings such as wall ties to the surface must also be added.
Then the total resistance is divided into one, to get a reciprocal resistance and this number is the U-value of the entire wall for example.
What are the consequences of misunderstanding U-values?
Since the materials may differ in their k-value even though they look the same, choosing the wrong material may have a bad effect on the U-value.
For example, a frequent site error is the selection of a narrow inner block for a cavity wall that may appear as specified.
This actually has a higher crushing strength and a worse (higher) k-value.
The resulting U-value may mean that the wall must then be lined internally with more insulation.
Perhaps under dry plasterboard to restore the U-value to where it should be.
For more architectural news
Ferring Pharmaceuticals completed with a canopy in Copenhagen


 العربية
العربية
Pingback: Building a Museum of Culture and History with stepped stone walls