Architectural acoustics are not the first thing on your mind when designing a building, most people may not notice acoustic problems until the building is inhabited.
Acoustic insulation need not compromise the design of the building, instead, consider the building’s acoustics early in the design process.
And there are a variety of materials, tools, and design techniques that can create a great listening experience that enhances design rather than compromising it.
There are three basic elements that architects must be aware of in architectural acoustic design.
absorption
Absorption is often referred to as soundproofing, although this is not technically correct.
While acoustic insulation is the process of keeping noise in or out of a space, absorption deals with the way noise is reflected back into a room.
Noise absorption also provides a way to dampen unpleasant noises in the environment. When a sound wave hits a hard, flat surface such as a wall or ceiling, it will reflect at an alternating angle, causing the sound to reverberate.
Absorbent materials trap noise within their pores and fibres, where sound is converted into heat and spreads throughout the material.
Common materials that absorb sound are acoustic panels, acoustic foam, sound deadening and acoustic cotton.

reflection
Most of us think of noise reflections as echoes, and reflection occurs when a sound wave bounces off a flat, hard surface.
Acoustic reflections become a problem in meeting rooms, auditoriums, and other large spaces due to the size and availability of reflective surfaces.
Clear sound is also important in each of these spaces, as audience members want to hear the presenter or performer clearly, and reverberation creates excessive noise that distracts the audience.
spread
One of the most important parts of creating a good listening experience is sound propagation. When audiences gather at conferences, speeches, or performances, they want to hear the full range of frequencies that come through the speakers.
Moreover, the audience members in the back of the room want to hear the action just as much as those in the front.
Sound diffusion ensures that high and low frequency sounds are transmitted evenly throughout the space.
If you’re designing a meeting room, boardroom, or office building with a speaker system, diffusion can help ensure that sound is transmitted evenly and without delay.
Sound-diffusing materials feature carefully calculated combinations of irregular surfaces, some thicker than others.
Irregular surfaces control the direction in which sound is reflected, variation in thickness controls the heading frequencies of materials, and thicker materials are considered more effective for lower frequencies.
The best soundproofing material
Soundproofing materials come in all shapes and types.
However, it is important to be aware of how and where to apply it to get the best results.
Needless to say, it is also important to consider the quality of the particular soundproofing material you intend to use in order to achieve the best possible results.
Here is a summary of the best soundproofing materials available on the market and how best to use them:

acoustic membrane
Different acoustic membranes on the market, some are much heavier than others and some are higher performing than others.
They will be rated by different decibel reduction levels across different Hertz frequencies and available in different thicknesses.
Thickness and weight will affect application and effectiveness, so it is important to choose well.
Uses: Ideal as a soundproofing membrane as it works well when it comes to reducing sound transmission.
Pros: Minimum depth to existing structures such as walls and ceiling, Easy to install, Long lasting.
The negatives: some are rather heavy with an increase in bulk which in turn provides the opposite effect, and some brands are more expensive.
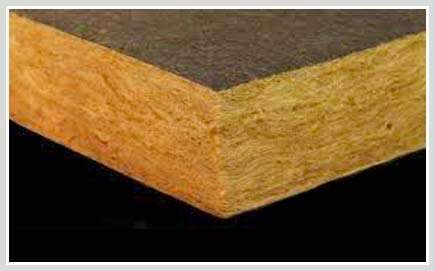
Acoustic mineral wool cavity insulation
Mineral, rock or stone, such as Quiet Fiber, are essentially open cell insulation materials that do very well at absorbing acoustic and thermal energies.
Often used in cavities such as stud walls, this solid material comes in various thicknesses and densities and is used in both homes and commercial projects because it is affordable.
Not only is it good at absorbing acoustic and thermal energy but almost as important if not more so,
it is very useful for filling cavities.
This prevents the cavity from being an open, resonant hole like a “cave” which can lead to amplification of acoustic energy.
Despite being very rigid, it is easy to cut.
Uses: For soundproofing walls and ceilings, making acoustic panels and bass traps,
and as soundproofing in various settings, from residential to commercial spaces.
Pros: affordable natural materials, fire and moisture resistant.
Cons: Needs a lot of depth for the material to be effective on its own,
Protective breathing equipment must be worn because cutting causes shrapnel to seep into the skin,
or may be inhaled and irritate the lungs.

Fiber glass
They are suitable for sound in sheets rather than rolls,
and can be used in a variety of settings and applications including making acoustic panels in home studios,
theaters and commercial buildings.
This soundproofing material is very effective at reducing noise entering or leaving a room,
and improves interior acoustics.
There are different types you can choose from with different thicknesses, density and strength.
For example, 703 plates are best for reducing high-frequency noise while 705 plates are more suitable for low-frequency bass noise.
Uses: In recording studios, home cinemas, theaters and anywhere where sound insulation is required,
they are extremely versatile.
Pros: Suitable for different frequency bands, comes in different thicknesses, and is easy to cut.
Cons: It is known to be an irritant so protective clothing should be worn when handling it.

Flexible channels
Flexible ducts are the primary method for separating drywall from the interior structures of buildings.
This system can also be installed with hangers or acoustic shims which further reduce vibration.
Flexible sound ducts are strips of metal or wood that are fixed to walls.
So that the sound insulation inside the walls can be kept firmly in place,
With the provision of a platform on which all finishing systems can be attached.
This eliminates direct contact that can be through the seams of the structure, walls, ceiling and floors.
The screws can pass through several holes or gaps in these channels to ensure easy tightening,
making it easy to install.
Any sounds that pass through will essentially vibrate against the flexible sound ducts,
thus isolating them from the room.
Uses: Generally used during construction as
it helps to achieve very good acoustic insulation in the building due to the principles of separation.
Pros: Relatively easy to install, no functional holes or holes
Cons: Low cost, installation will take a long time if there is a large area to cover.
The use of colors in interior design













