Chenée School Design: Integrating Diverse Learning, Spatial Organization, and Energy Efficiency
A Contemporary Educational Approach
The design of the new school in Chenée is based on a modern educational methodology. The importance of spaces extends beyond traditional classrooms to include both indoor and outdoor communal areas. This design reflects a deep understanding of the role of the environment in supporting learning and developing students’ skills.
Informal Learning and Social Interaction
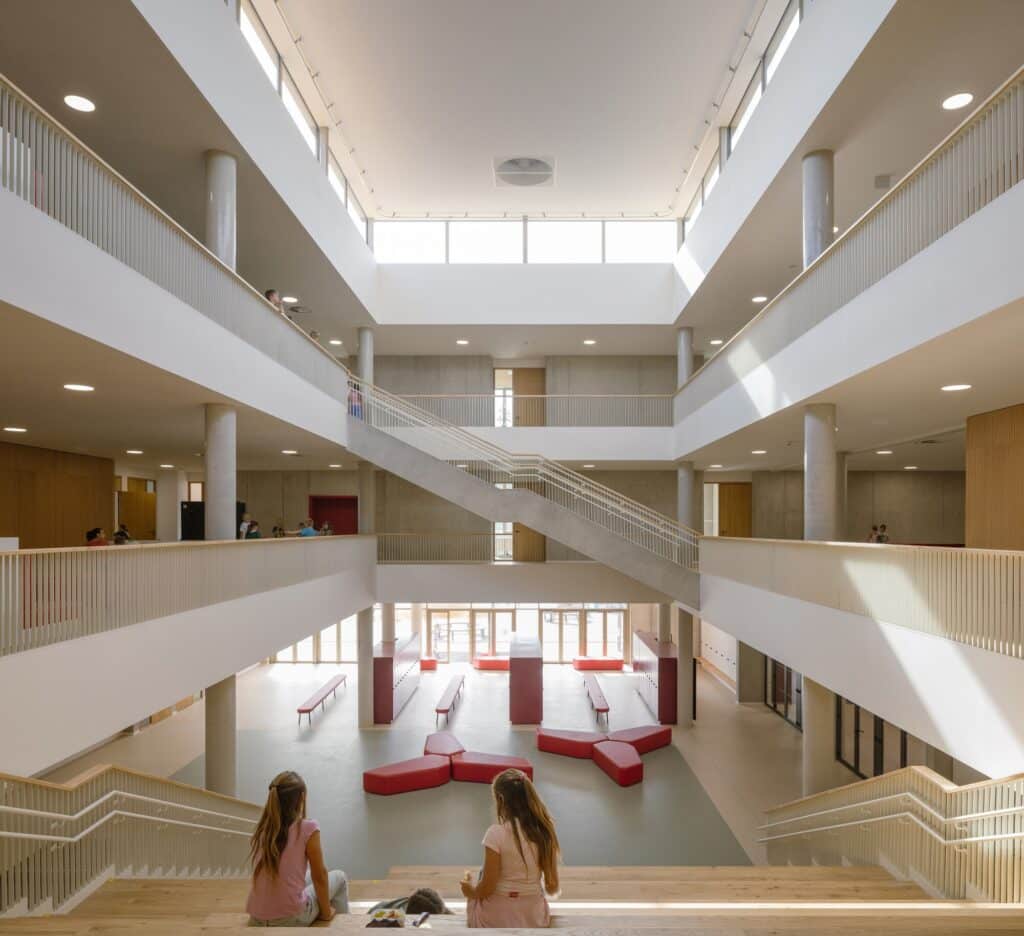
The alcoves along the corridors provide opportunities for informal learning, where students can interact and exchange knowledge outside the classrooms. Additionally, small corners offer suitable spaces for quiet discussions, encouraging independent thinking and enhancing communication skills.
Flexible Classroom Arrangements
The classrooms feature diverse seating arrangements that support different focus styles, allowing students to choose the environment that best facilitates their learning. This flexibility in interior design reflects an approach centered on the needs of each student individually.
The Roof as a Multipurpose Space
The rooftop is designed as a space for both play and learning, providing opportunities for interactive activities that combine physical education with hands-on experiences.
A Rich Learning Environment
In this way, the school offers a diverse internal world where both young children and adolescents can find spaces that suit them, fostering a sense of comfort and belonging during the learning process.


Multi-Use Spaces After School Hours
The building’s role extends beyond primary education to encompass a variety of afternoon programs. For instance, the school offers extracurricular activities for students, contributing to the development of their personal and social skills outside the traditional academic framework.
Supporting Lifelong Learning for Adults
In addition, the school hosts educational and sports activities aimed at adults, reflecting the design’s commitment to providing a continuous and versatile learning environment for all community members. This approach maximizes the building’s utilization and helps foster an active and educated community.
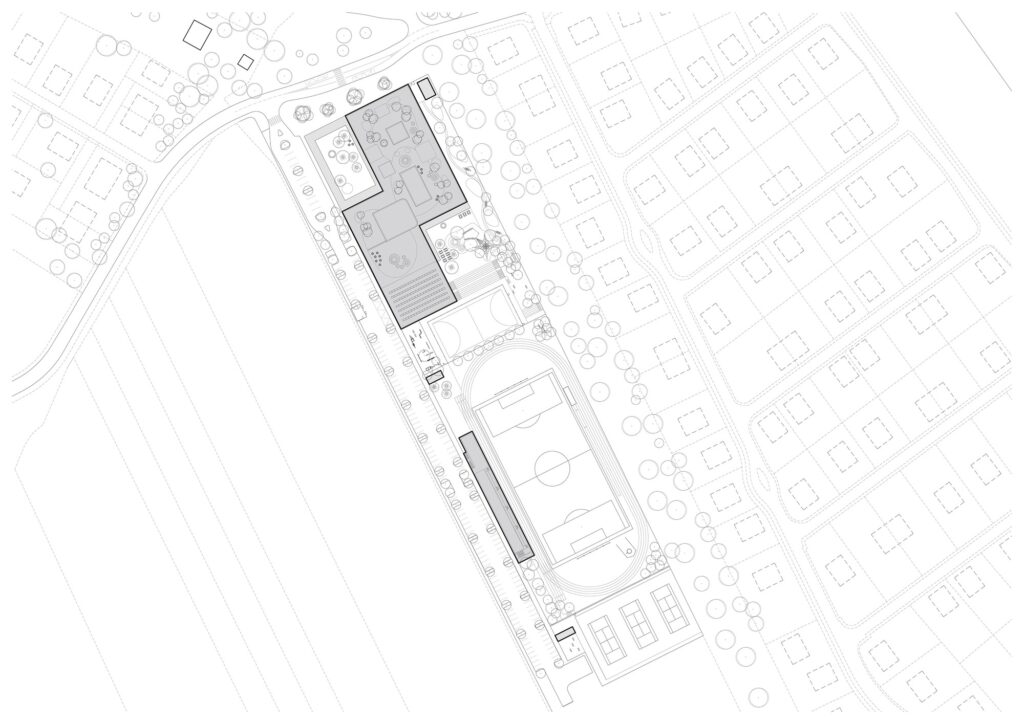
Geographical Location and Urban Context
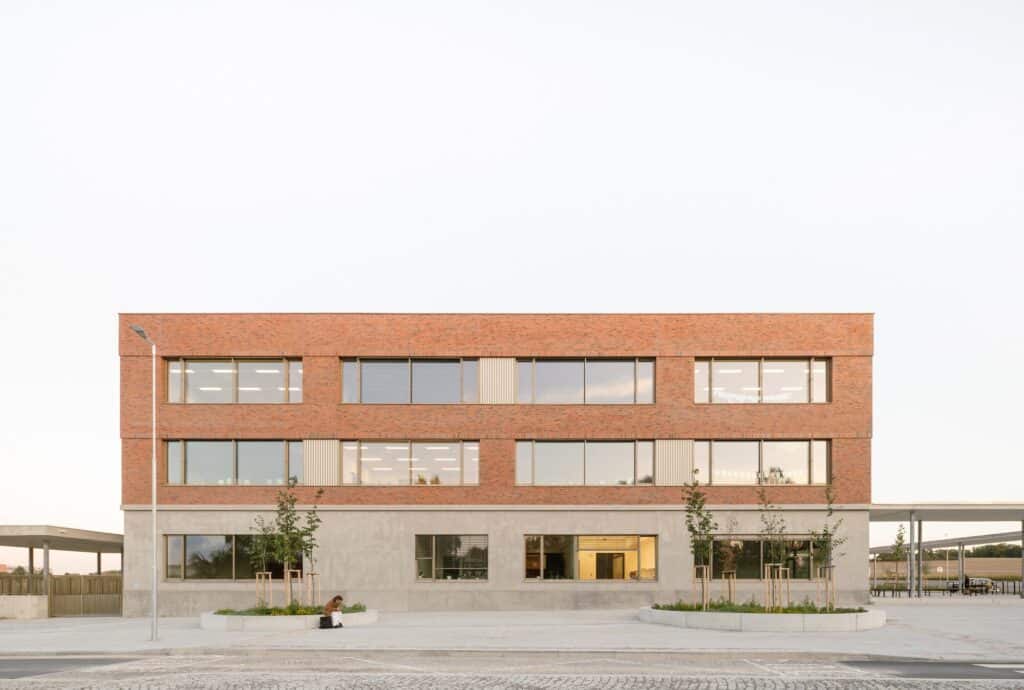
The elongated and sloped site is located near the center of the town of Chenée, a rapidly growing municipality close to Prague. This strategic location makes the building part of a transforming area, whose surroundings are expected to experience significant residential development in the near future. More information on similar cities can be found in our archive.
Balancing Isolation and Integration
In the short term, the new school may stand alone in the field at the edge of the town, giving it a sense of temporary isolation. Over time, however, it will become an integral part of the urban fabric, reflecting a gradual integration into the surrounding environment.
A Design That Embraces the Future
In response to these challenges, the design aims to address both conditions, the current isolation and future urban integration, while providing a clearly defined and easily recognizable public space. This approach ensures that the building remains functional and appealing both in its initial phase and as the surrounding area develops.

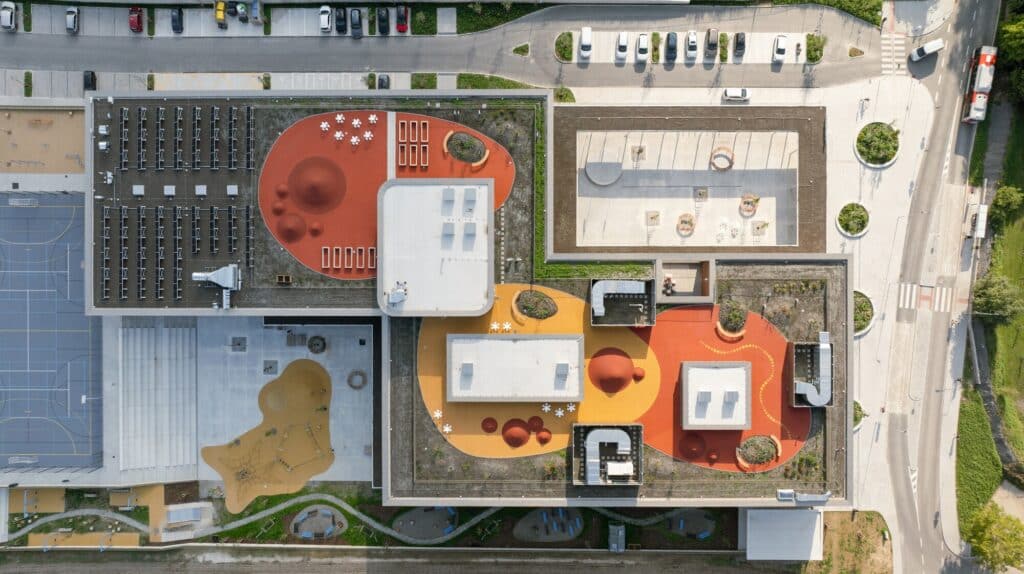
Organizing the Building Around Two Courtyards
The building’s master plan is based on the concept of two courtyards, one public and one private, which helps organize the spaces in a way that balances different uses.
The Public Courtyard and Communal Spaces
The northern part of the building houses the classrooms and the main communal area, creating a comprehensive learning environment that encourages student interaction and facilitates movement between classrooms and shared spaces.
The Private Courtyard and Supporting Facilities
In contrast, the southern part contains sports facilities, a multipurpose hall, and supporting service areas. This layout ensures that recreational and athletic activities are separated from educational spaces, while maintaining the functional coherence of the building.

Vertical Articulation of the Building
The school consists of three floors, and the vertical articulation has been designed in response to the site’s slope. This approach allows for a dynamic use of the location and provides different opportunities for accessing the building.
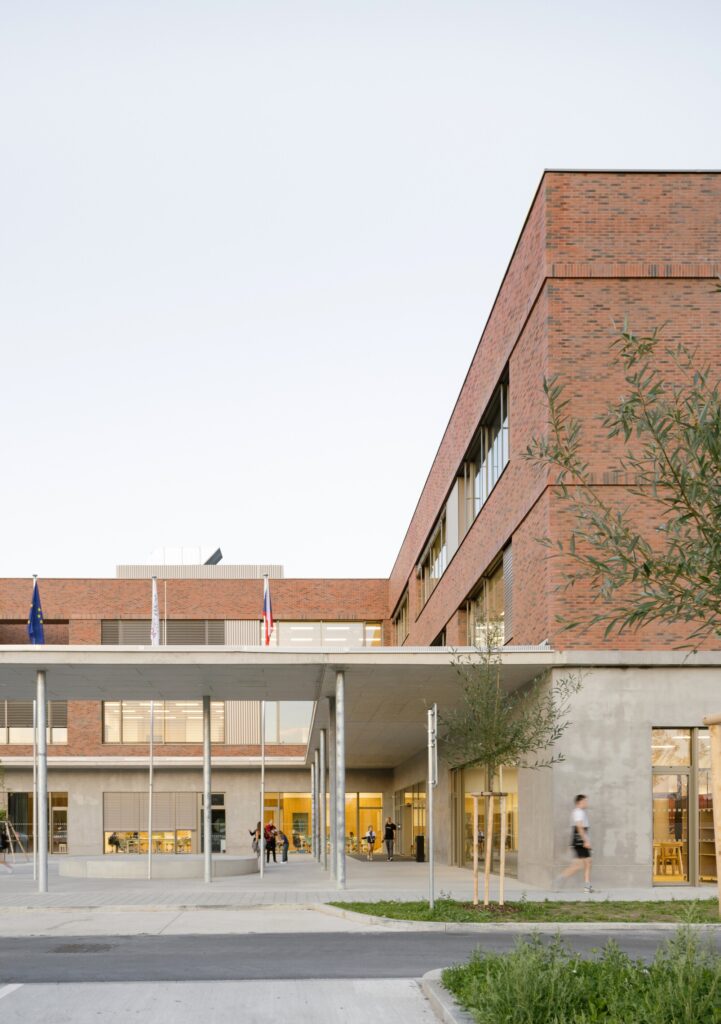
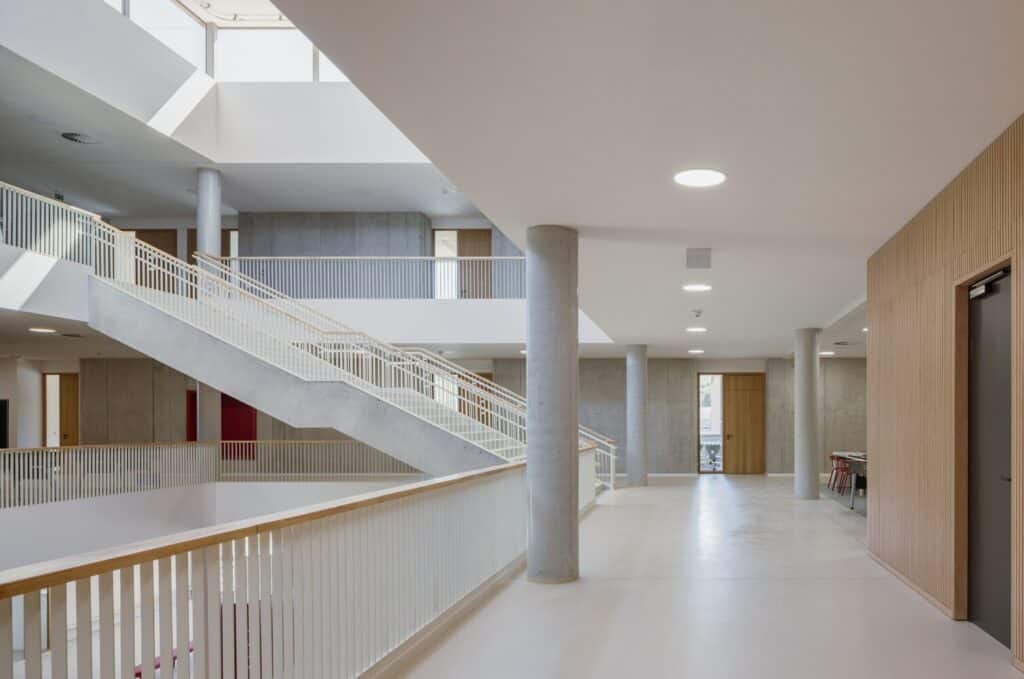
Easy Access from Different Levels
Direct access to the building is not limited to the ground floor when coming from the town center; it is also available from the first floor, which connects to the sports complex. This enhances movement flexibility within the school and strengthens its connection to external facilities.
Upper Floors and Outdoor Spaces
On the third floor, an outdoor classroom is proposed, providing direct connection to external spaces from every level. Additionally, the rooftop includes an outdoor terrace, classrooms, and planting beds dedicated to gardening activities, fostering experiential learning and encouraging students to interact with their surroundings. Related building materials contribute to sustainable construction.

Building Operational Patterns
The building can operate according to two main patterns, reflecting the design’s flexibility and its responsiveness to the varying needs of users.
Full Morning Operation
During the morning teaching period, the entire facility is open and fully utilized, allowing maximum use of educational spaces and associated activities.
Partial Afternoon Operation
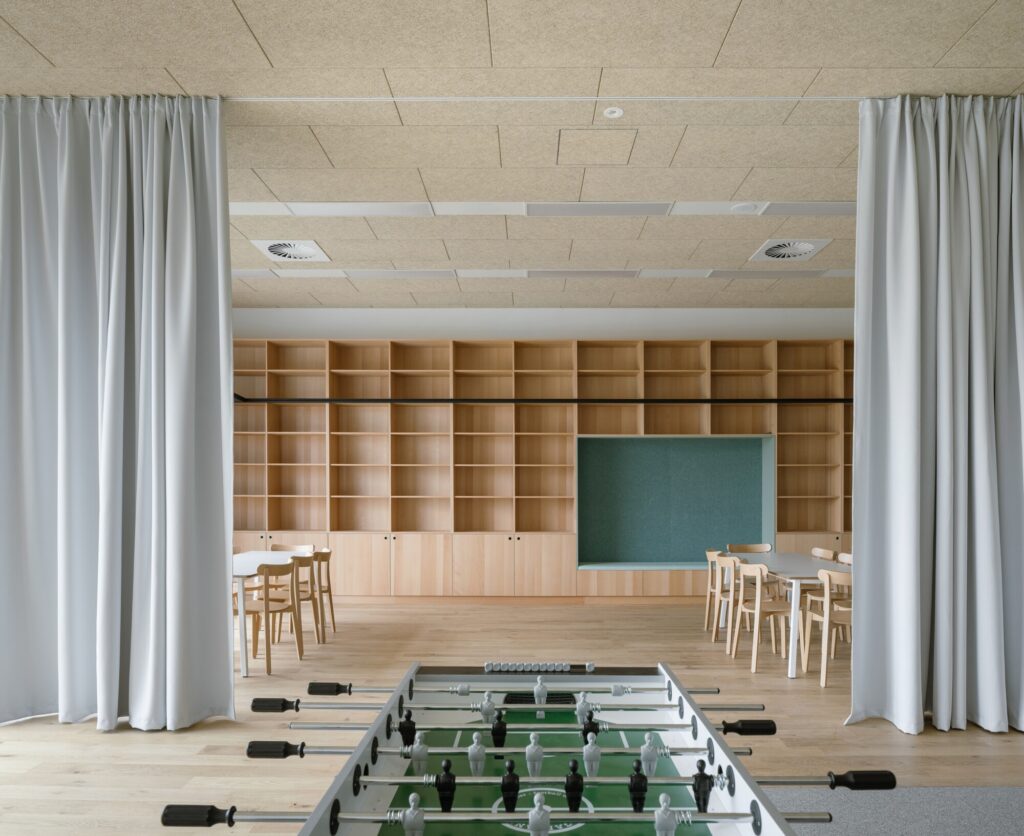
In the afternoon, a partial operational mode is adopted, granting public access only to specific parts of the building. These include areas designated for activities and clubs, the library, the gymnasium, and the multipurpose hall. This hall can also host occasional cultural events, reinforcing the building’s role as a comprehensive community activity center.
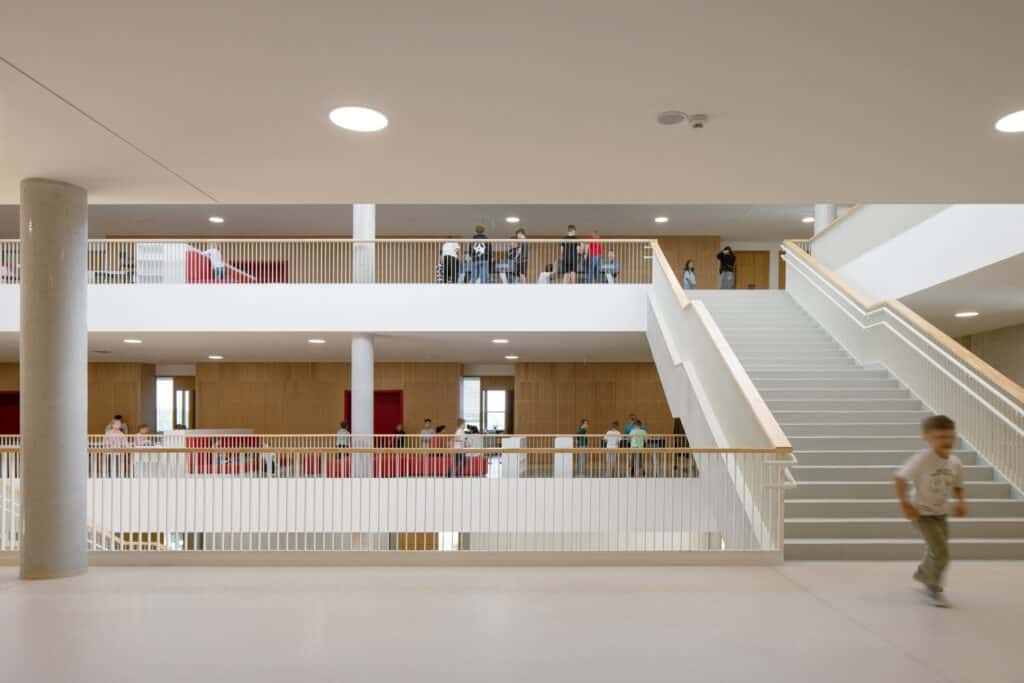
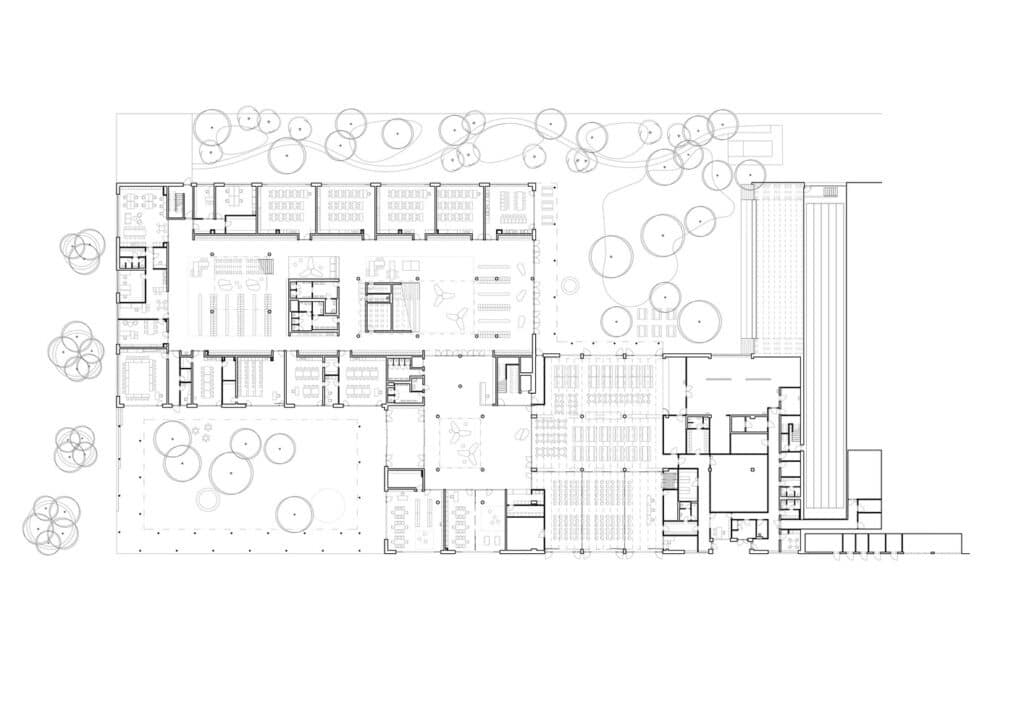



Organizing the School Grounds by Elevation Levels
The school grounds are arranged on two main levels within the sloped site, reflecting the design’s response to the terrain and its functional and aesthetic use.
The First Level and the Two Courtyards
The first level corresponds to the school’s main floor and includes the two courtyards, public and private, facilitating access to classrooms and communal spaces, and creating a clear hierarchy among different educational functions.
The Upper Level and the Sports Complex
The second level is situated one floor above the first and accommodates the sports complex. This arrangement ensures the separation of athletic activities from educational spaces, while maintaining the site’s cohesion and providing direct access between the school’s different levels.

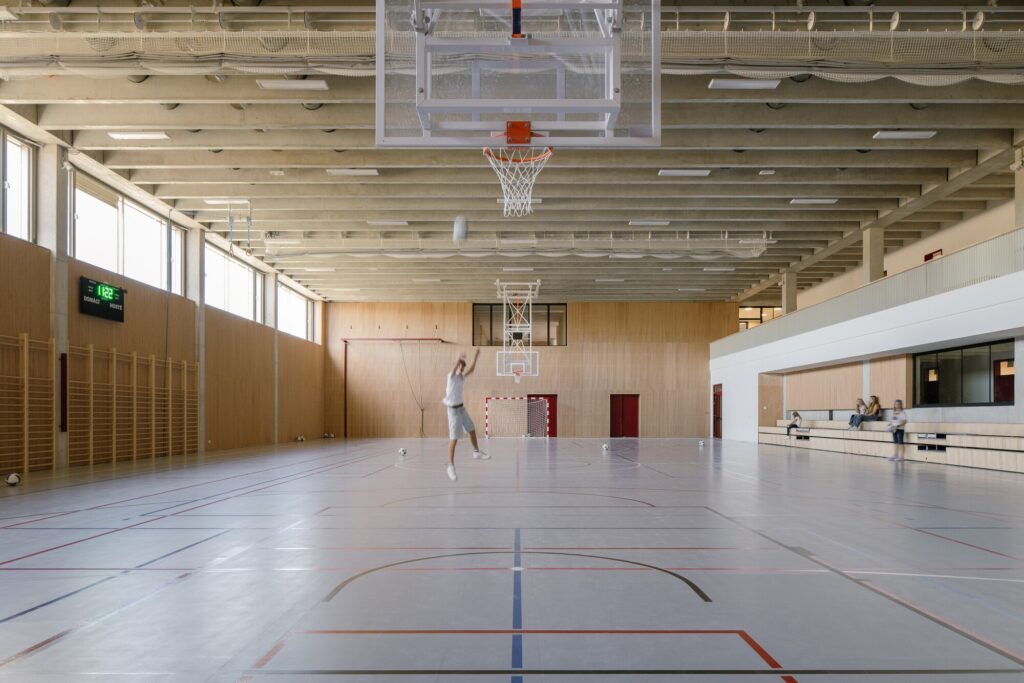
Sports Facilities of the Building
The sports complex includes several integrated fields, including an athletics track directly connected to the football field, reflecting a design that allows multiple uses and enhances the variety of sports activities.
Supporting Facilities and Amenities
In addition to the fields, the complex houses supporting service facilities, a sports tunnel, and a refreshment area along the eastern side, contributing to user comfort and ensuring smooth circulation during events.
Spectator Areas
Dedicated spectator areas are provided, both along the seating adjacent to the track and on the roof of the facilities building, which serves as a viewing stand, allowing activities to be followed comfortably and safely.
Secondary Training Field
A secondary training field is located between the school building and the track, and it is also available for use during school breaks, enhancing daily sports opportunities and serving all student groups.
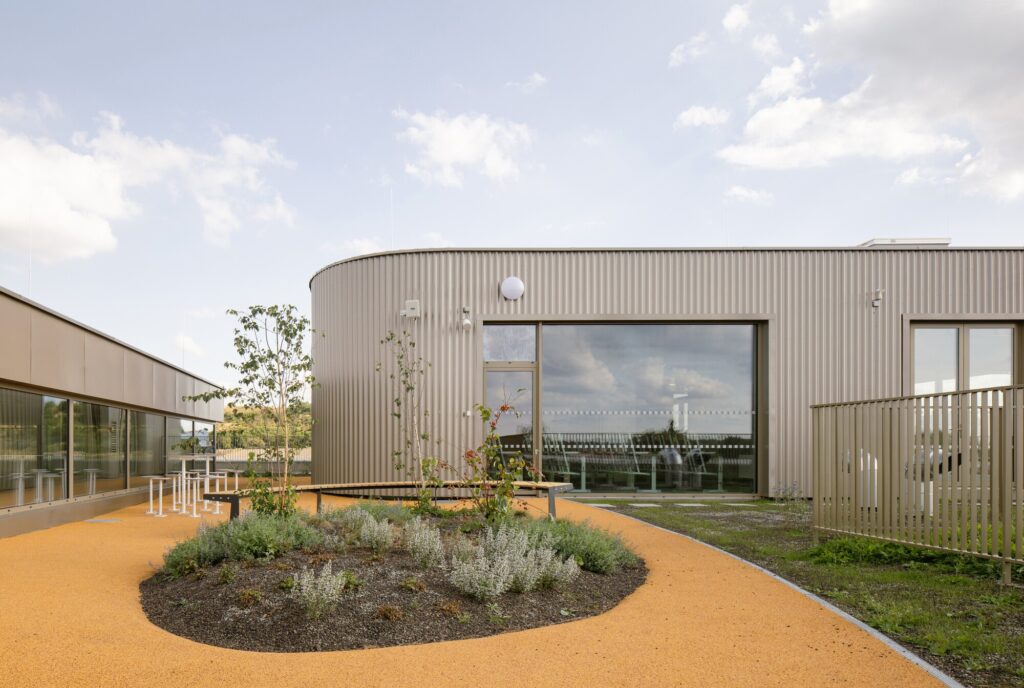

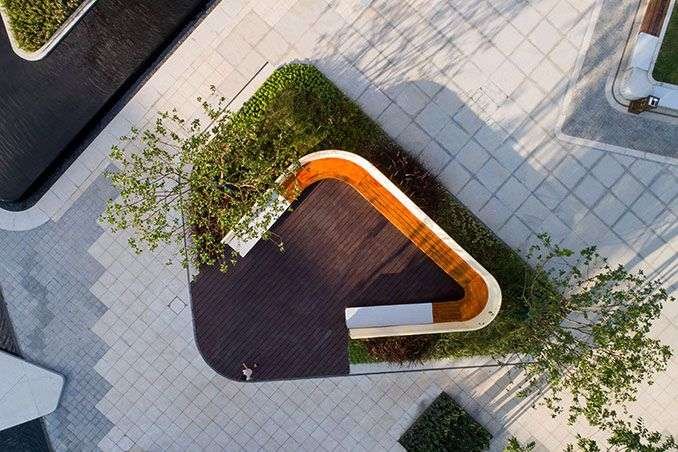
Courtyard One: Entrance and Reception for Learners and Visitors
The entrance courtyard serves students and visitors participating in afternoon programs as well as the general public. It includes seating areas for teenagers and sports spaces specifically designed for younger students, enhancing opportunities for social interaction and physical activity.
Courtyard Two: Dining and Recreational Activities
The second courtyard features outdoor dining tables, expanding the cafeteria’s capacity and providing a comfortable environment for meals. It also offers space for play during breaks and for recreational activities linked to the afternoon programs.
Play and Physical Activity Facilities
Multiple play structures have been integrated, including soft surfaces for jumping and running, a rope pyramid, and other equipment, contributing to the development of children’s motor skills and encouraging physical activity in a fun and safe way.
Ease of Access and Connectivity Between Spaces
Access to the inner courtyard is available from the school hall, the cafeteria, and the training kitchen, creating functional connectivity between different spaces and facilitating the courtyard’s use at various times throughout the day. Additional architecture elements enhance this integration.

Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
The school is designed to meet Class A energy efficiency requirements, reflecting the project’s commitment to sustainability and reduced energy consumption.
Heating and Ventilation Systems
Heating is provided by heat pumps, while all spaces are equipped with controlled mechanical ventilation, with natural ventilation also available in each occupied space through operable windows. This balance between mechanical and natural ventilation enhances user comfort and reduces reliance on energy systems.
Energy Balance and Complementary Technologies
Photovoltaic panels installed on the roofs of both the main building and the sports complex contribute to the overall energy balance. Additionally, the use of external shading and high-quality thermal insulation helps reduce energy loss, supporting long-term sustainability.
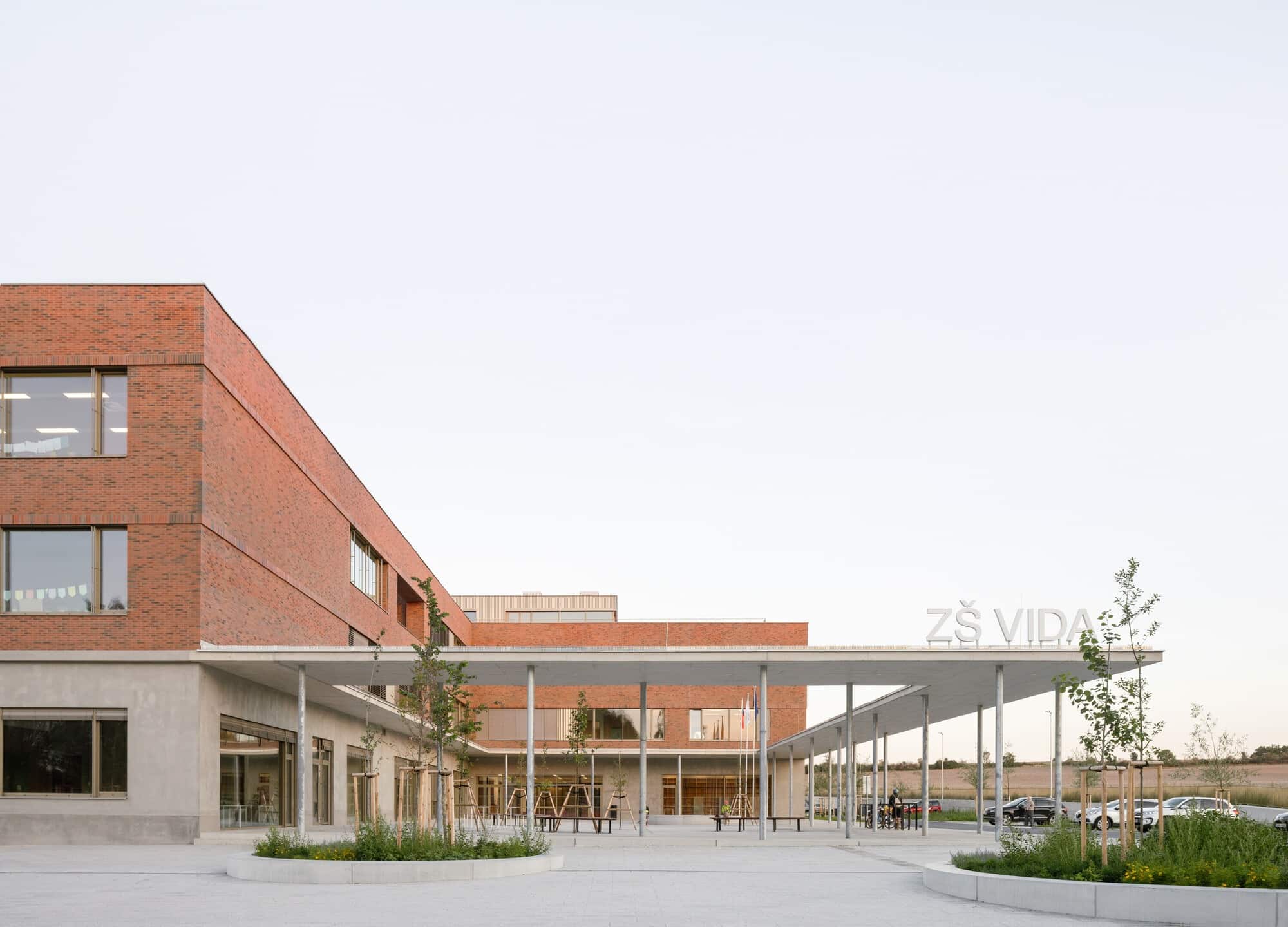
Structure and Facade
The building relies on a reinforced concrete structure with masonry infill, providing strong thermal mass and structural stability. The exterior facade is clad with ceramic elements, while rooftop shading and planted tree nests help reduce the formation of heat islands, improving the surrounding environment’s quality and enhancing thermal comfort.

✦ ArchUp Editorial Insight
The Chenée school project represents an architectural experiment exploring the integration of formal and informal learning and the organization of spaces across different levels. Among its strengths, one can observe the flexibility of classroom arrangements and the provision of multiple activity areas, offering opportunities for interactive learning and hands-on experiences. Additionally, the response to the site’s slope and the use of the rooftop as a learning space reflect an awareness of the natural environment and a commitment to sustainability.
However, the project may raise several questions regarding long-term operational efficiency, particularly concerning the management of movement between different floors and the use of multiple courtyards at various times of the day. The wide diversity of spaces may also require careful monitoring to ensure optimal utilization of all areas, especially when combining activities for different age groups. Furthermore, the focus on sustainable energy performance may present challenges in terms of maintenance and cost compared to traditional schools, necessitating ongoing evaluation to balance innovation with practical efficiency.
Despite these reservations, the project provides a valuable platform for studying methods of integrating diverse educational spaces and applying sustainability principles. It can serve as a reference for future designs seeking to achieve a balance between learning, social openness, and environmental efficiency.
Project information
- Architects: OVA
- Area: 5175 m²
- Year: 2025
- Photographs:Alex Shoots Buildings





ArchUp: Technical Analysis of the Qinyeh School Design
This article provides a technical analysis of the Qinyeh School as a case study in high-performance, flexible educational architecture. To enhance archival value, we present the following key technical and design data:
The design layout is based on a dual-courtyard configuration: a northern public courtyard for classrooms and interactive spaces, and a southern private courtyard for sports and service facilities. This strategy utilizes the site’s natural 6% slope to create two main entrances at different levels, with a total built area of approximately 8,500 square meters.
The project is distinguished by achieving Class A energy efficiency standards through an integrated system. Geothermal heat pumps serve as the primary source for heating and cooling, while rooftop photovoltaic panels generate up to 40% of the building’s electricity needs. This system is supported by high-quality thermal insulation and windows with a U-value below 1.0 W/m²K.
In terms of functional performance, the design integrates three smart operational modes. During school hours (7 AM – 2 PM), all facilities operate at full capacity. In the afternoon (2 PM – 6 PM), 60% of the spaces (library, hall, lounge) are opened for community activities. The educational rooftop, equipped with planting beds and natural lighting, provides additional learning spaces, increasing capacity by 15%.
Related Link: Please refer to this article for a comparison with other educational projects focusing on flexibility and sustainability:
Cultural Transformation: Redefining the Relationship Between Civic, Cultural, and Social Functions
https://archup.net/dusseldorf-opera-house-opening/