Curtain Wall When the Facade Becomes a Smart, Functional Element of Modern Architecture
The curtain wall has redefined what it means for a façade to be more than a skin transforming it into an intelligent, high-performance layer that mediates between environment, structure, and space. Once purely aesthetic or symbolic, today’s curtain walls are multifunctional systems that balance transparency, insulation, and structural agility. Technically, a curtain wall is a non-load-bearing envelope attached to the building frame, often composed of glass, aluminum, or high-performance composites. But in modern applications, especially post-2000, these systems evolved into climate-responsive façades that can reduce a building’s energy consumption by up to 30%, according to the International Energy Agency. Iconic examples like the Al Bahar Towers in Abu Dhabi, featuring a responsive mashrabiya system, or Apple Park’s 4-story curved glass panels, illustrate how curtain walls are now mediators of daylight, thermal comfort, and aesthetics. With the integration of photovoltaic glass, double-skin systems, and dynamic shading, curtain walls are being engineered to adapt in real-time to solar exposure and ambient temperatures. In cities like Singapore and Toronto, regulatory incentives now push developers to use high-efficiency façades, spurring innovation in low-emissivity coatings, triple glazing, and vacuum-insulated units. Curtain wall systems, once reserved for skyscrapers, are now found in cultural institutions, airports, and even sustainable housing, blurring the line between envelope and interface. As architectural thinking moves toward performative design, the curtain wall becomes not just a visual statement but a responsive membrane a technological organ breathing with the city.
In recent years, curtain walls have become one of the most essential components in modern building design. No longer just an outer shell, they’ve evolved into a sophisticated system that blends functionality with aesthetics playing a central role in high-end architectural projects around the globe.

What Exactly Is a Curtain Wall?
A curtain wall is a lightweight exterior facade that doesn’t carry the structural loads of the building. Instead, it’s attached to the building’s framework and only supports its own weight, along with wind pressure and environmental forces.
Think of it as the skin or “outer layer” of a building an element designed not just for looks, but also to protect the interior from weather conditions like rain, wind, and temperature changes, all while enhancing visual appeal.
Why Has the Curtain Wall Become So Popular?
Because it offers more than just good looks. Curtain walls bring a range of practical benefits:
- Energy Efficiency: Using insulated glass or materials with thermal properties helps reduce reliance on air conditioning and heating.
- Natural Lighting: Glass facades allow daylight to flood interiors, cutting down on artificial lighting needs and creating healthier spaces.
- Modern Aesthetic: Sleek glass or metallic finishes give buildings a contemporary, eye-catching appearance.
- Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Especially with pre-fabricated systems, where panels are made off-site and installed ready-made, reducing time and errors on site.
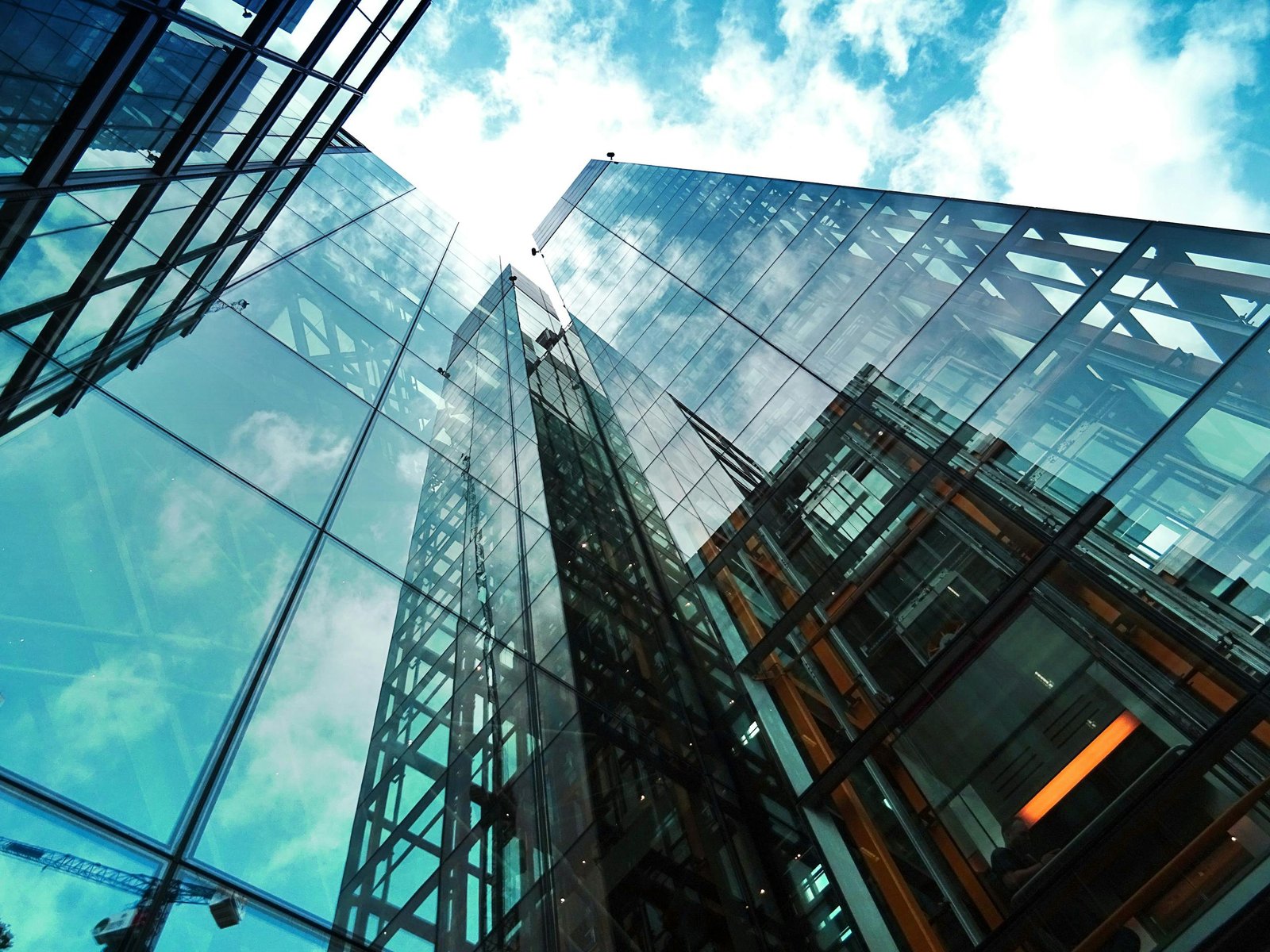

Materials Commonly Used in Curtain Walls
| Material | Use |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | Most commonly used for vertical (mullion) and horizontal (transom) framing. It’s lightweight, durable, and resistant to corrosion. |
| Glass | One of the most popular choices—can be single, double-glazed, tempered, or reflective glass. |
| Metal Panels | Like stainless steel or coated aluminum panels, often used for non-transparent sections. |
| Plastic or Composite Materials | Such as laminates or polymers, used for decorative details or specific parts. |


How Are Curtain Walls Installed? Different Systems Explained
There are several installation methods for curtain walls, each suited to different project types and design needs:
1. Panellised Curtain Wall A large, pre-assembled unit made in a factory and then installed fully on-site. Quick and easy to install, ideal for large-scale developments.
2. Unitized Curtain Wall Pre-fabricated units of varying sizes that are mounted directly onto the building structure. Offers high precision and is widely used in high-rise towers.
3. Stick System Each component the frame and glass is assembled piece by piece on-site. Allows greater design flexibility but takes more time to complete.
4. Rainscreen System Includes an air cavity between the outer and inner walls, improving insulation and preventing water infiltration.
5. Spider Glass System Uses metal bolts to attach glass panels directly to a structural frame. Often used in commercial spaces or buildings requiring full transparency.


Types of Curtain Walls Based on Sealing and Performance
| Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Sealed System | Relies on tight joints between panels to prevent air and water penetration. | Dry and cold climates. |
| Drained System | Includes internal drainage channels to guide away any water that gets through. | Rainy or humid areas. |
| Pressure Equalized System | Uses an air cavity to balance pressure between inside and outside. | High-end, tall buildings where performance is critical. |
Engineering Challenges: Are There Any Drawbacks?
Of course. Despite their many advantages, curtain walls do come with some challenges:
- Light Pollution: Reflective glass can cause glare and increase surrounding temperatures.
- Maintenance Complexity: Especially for high rise buildings, which require special equipment for cleaning and repairs.
- Coordination with Structural Design: Must align precisely with the building’s internal framework.
- Higher Costs: Particularly for advanced systems like spider glass or rainscreens.

The Future: Smarter, More Intelligent Curtain Walls
Technology is pushing curtain walls even further. We’re now seeing innovations like:
- Smart Glass that adjusts light and heat transmission based on climate.
- Solar Facades integrating photovoltaic cells to generate power.
- Living Facades incorporating greenery or air purification systems.
These developments suggest that curtain walls will play a key role in shaping the smart, sustainable buildings of tomorrow .
Final Thoughts
A curtain wall isn’t just a stylish glass front it’s a comprehensive engineering solution that balances form and function. As cities grow and sustainability becomes more urgent, curtain walls will continue to evolve, becoming smarter, more efficient, and more integrated with building systems.
Want to know how you can apply curtain walls in your next project? Stay tuned for our upcoming articles, where we’ll explore top manufacturers of curtain wall systems in the Arab world and the latest technologies available in the global market.
At ArchUp, we believe the future of construction isn’t just about how things look it’s about how well they perform, how efficiently they operate, and how responsibly they interact with the environment. And the curtain wall is one of the clearest examples of that vision becoming reality.