Hydronic Heating: Everything You Need to Know
Unlike traditional heating systems that warm the air, hydronic heating systems heat a liquid that is a good conductor of heat. It helps make the system more efficient and warm different areas of the house as per varying requirements.
Even though it takes some time for the system to achieve the desired temperature, hydronic systems are easier to use and prove low maintenance. Keep reading to know how they work and what makes them unique.
What Is A Hydronic Heating System?
A hydronic heating system is a highly versatile and efficient heating system, using a hot liquid like water or oil to keep your home warm. This hot liquid is first heated and then circulated through pipes that take it around the house for proper heating.
Meanwhile, the cool liquid is sent back to the heater, and the process is repeated. The type of heater people use varies, depending on their requirements, with one of the most common being boilers.
Boilers heat the liquid, which in turn heats the surface of the pipes and helps raise the temperature of the ambient air. You should know that hydronic heating systems are also called radiant heating systems since the heated water travels through to the pipes of underfloor heating systems, like panel radiators and trench convectors.
What makes hydronic systems popular is they heat various objects in the room and not the air. Hence, you can reduce fluctuations or cold spots to get even heat distribution.
You can install hydronic heating in the floors, within concrete foundations, over existing flooring, and by opting for prefabricated panels.
Understanding Hydronic Heating Systems
We have mentioned how the heat radiating from the pipes in hydronic heating systems helps keep various rooms across the house warm. But the key element in ensuring the system performs effectively is water or another liquid that is a good conductor of heat.
Since air is an excellent conductor of heat, hydronic systems use thermal radiation to heat a room. For those who don’t know, it involves the transfer of heat by using air as a medium, thanks to electromagnetic radiation waves.
Moreover, this radiant heat is absorbed by different objects and doesn’t blow away as in other forms of heating. For instance, each trench in a trench convector system has special panels that are heated by the hydronic system.
Cool air within the room descends into the trenches and rises up again after being heated through the grilles.
Components Of A Hydronic Heating System
For a further understanding of hydronic heating systems, read about the main components in this section to know how everything functions.
A. Heating System
The central heating system is responsible for heating the fluid, and several heaters can be used for this purpose, like heat pumps, oil or natural gas boilers, solar heaters, and wood furnaces. Also, what heat source you use depends on the demands of your home.
B. Distribution System
Thanks to the distribution system, fluid is pumped into the heat exchangers, from where it again goes to the heating system. Some of the components of a distribution system include –
- Thermostats
- Pipes
- Pumps
- Valves
C. Heat Exchange System
With the heat exchange system, the heat from the heated liquid is circulated around the house. Thermal radiation and natural convection help heat the fluid until it’s hot.
While radiation systems directly heat the air, natural convection causes hot air to rise. Sometimes, the hot liquid heats an object, which in turn heats the air.
D. Other Components
Some other units of a hydronic system you must know about are –
1. Piping
The pipe system is made of multilayered composite, plastic, or copper for the best results. Heated water travels through the pipes to the radiators, underfloor heating coils, and convectors from the boiler before traveling back again.
2. Boiler
The boiler heats the water to the predetermined temperature and runs on several fuels, such as natural gas, off-peak electricity, LPG, wood pellets, and diesel.
3. Pump
The pump is responsible for circulating fluid through the pipes.
4. Convectors And Radiators
Radiators and convectors transfer heat across the house and into various rooms. You can choose your preferred convector or radiator model, depending on the budget and layout.
5. Thermostat
These systems also have an adjustable wall thermostat to manage the temperature and heat levels within a room for optimum comfort. Most modern thermostats have zone control, helping you heat specific rooms and alter the temperature of different areas in the house.

Types Of Hydronic Heating Systems
In this section, we have highlighted the types of hydronic heating systems you must know about.
1. Hydro-Air Heating
A hydro-air heating system uses forced-air heating with Hydronics to warm your home. The boiler kicks things off by heating the water and pumping it into the air handler of the furnace.
This water passes through the heating coil, following which heat transfers into the air within the furnace. Then a fan pushes the heated air using a duct system and helps keep your home warm.
You can use hydro-air heating with a tankless water heater to use the hot water for daily chores. But you will need a professional to install the system and the necessary equipment.
2. Baseboard Heaters And Radiators
Radiators and baseboard heaters are self-contained units featuring the components of a central heating boiler system and internal liquid reservoirs. You will find metal fins around the reservoir or water pipe that help distribute heat throughout the room.
When heat from the unit rises, it warms the surrounding objects and the air.
Traditional radiators are used to circulate steam after heating the water in the boiler, but modern radiators use electric pumps to circulate hot water. It’s not surprising that hot water radiators are one of the most common heat sources in US homes.
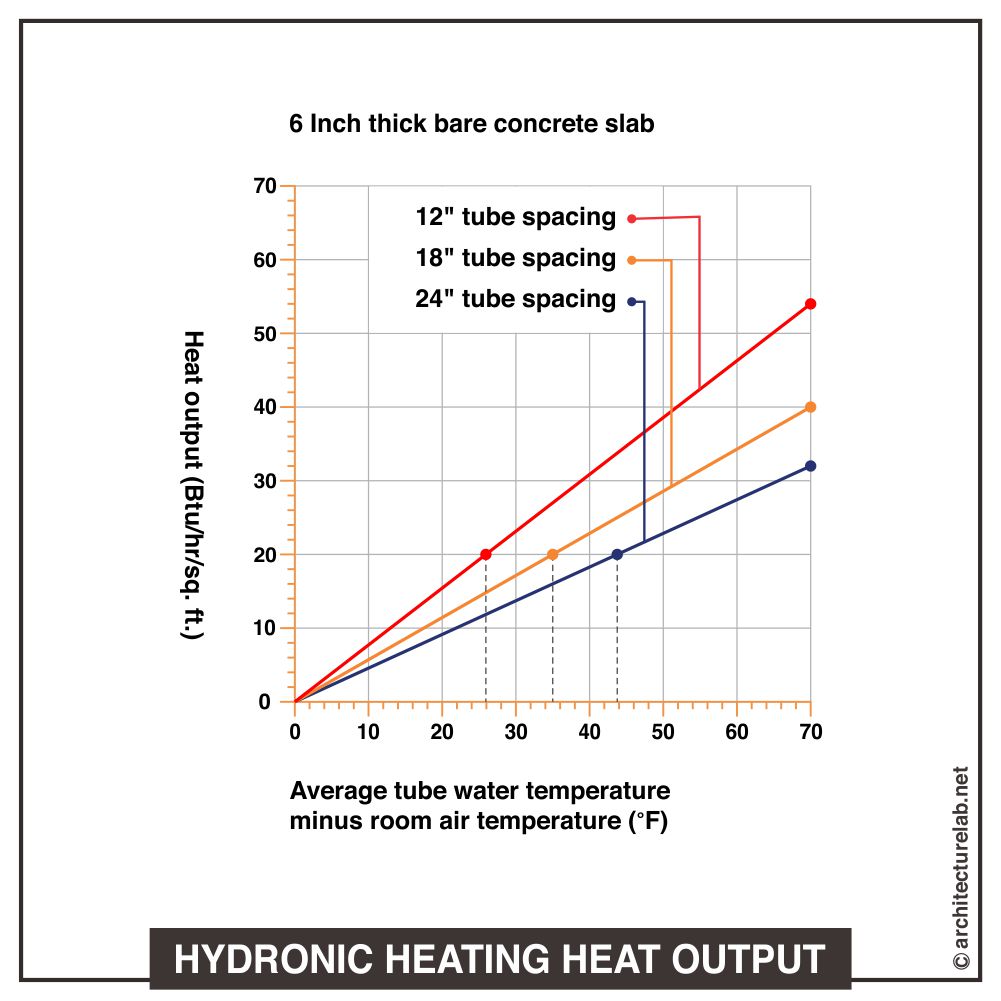
3. Radiant Floor System
This is the most common type of hydronic system, whereby the heated liquid travels through pipes laid underneath the flooring. The heat from the liquid passes to the floor, objects, and the surrounding air.
For greater efficiency, most homeowners opt for wet floor installation by covering the tubes in concrete or other materials over the subfloor. Another method is dry floor installation, which involves laying lines in the space below the floor or using joists to suspend them.
You can also use tile, concrete, or wood to design the flooring, and radiant floor systems are even available as ceiling or wall systems.
Types Of Heaters In Hydronic Heating Systems
Since hydronic systems work by heating a hot fluid, you might be wondering what heaters are used in the process.
1. Tankless Water Heater
Tankless water heaters don’t have a hot water storage tank like traditional water heaters. Instead, they come with a gas burner or use electricity to heat the water on demand.
Since the water is directly heated in the pipes, you get an unlimited supply of hot water. The biggest advantage of using tankless heaters is their efficiency because they don’t lose heat due to standing water.
They also occupy less space, but the initial cost of installing such systems is a bit high. Moreover, it takes a little time to heat the water unless demands surpass the actuation level.
2. Solar Water Heater
These heaters produce hot water using the sun’s energy and deflect sunlight onto a hot water storage tank. Solar heaters have low operational costs and hardly require maintenance while having a warranty of 20-30 years.
However, they are most effective in regions that receive sufficient sunlight throughout the year, work on slightly costly batteries, and need ample roof space.
3. Heat Pump
Heat pumps can heat houses and water with the water tanks working like heaters. It’s like a refrigerator, but the coolant absorbs heat in this case and uses it to heat the water in the tank after passing the liquid through the coils filled with coolant.
People opt for such heaters because they are easy to use and highly efficient, while you can enjoy rebates and tax incentives. But they work best in mild climates as they fail to generate sufficient heat to warm radiant floors.
4. Combi Boilers
These are much like tankless water heaters and use gas burners to quickly heat the water when needed. Moreover, the hot water is safe for household purposes.
Best of all is the small size of these boilers since they don’t use tanks and can be set up inside cabinets. But these efficient units fail to deliver the best result if they are supplying water to multiple appliances simultaneously.
Plus, your home must get a consistent supply of hot water for combi boilers to work.
Benefits Of Hydronic Heating Systems
Here are some of the most popular reasons why people use hydronic heating systems.
1. Separate Zones
One of the biggest hydronic heating benefits is they create temperature zones to increase comfort. This means instead of having one consistent temperature throughout your home, you can create separate temperature zones and adjust the temperature accordingly.
This is highly convenient because people have varying preferences. You can even create separate zones in a room when one person likes it warm, and the other likes it cool.
Moreover, you won’t have to worry about temperature variations even when the doors or windows are open.
2. Humidity Control
Unlike forced-air systems, radiant heat doesn’t make your home dry. Whereas forced-air systems remove moisture from the air and create unbalanced humidity, radiant heat involves circulating the liquid in a closed system, which doesn’t affect humidity levels.
3. Warm Floors
Thanks to radiant heating, the floors of your house will be warm, which is highly convenient when you roll out of bed on a cold morning. The tubes below the floor keep the surface warm, while the floors keep various objects warm in your room.
4. Quiet
The convenience of radiant heating systems is further enhanced because they are quiet and hardly make any noise. Compared to other heating systems, you won’t be disturbed by the sound of a furnace or the creaks and groans of hot air traveling through cool ducts.
In fact, they are much like thermal curtains that reduce heat transfer and keep the cold air out. High-quality curtains must drop down to floor length and cover the width of the window to keep your home comfortable in winter.
When used in conjunction with hydronic systems, you can maintain a comfortable temperature easily.
5. Ductless
Hydronic systems don’t use ducts or return-air systems. This saves a lot of space in your home, especially under the walls and ceilings, while retrofitting air ducts in homes after moving in can prove messy and expensive.
But in hydronic systems, these tubes can be hidden within walls, diverted around the existing piping, or attached to joists.
Drawbacks Of Hydronic Systems
Despite their many advantages, there are certain drawbacks to a hydronic system, and we have discussed some of these points below.
1. Longer Heating Time
Hydronic systems take longer to heat your home despite water absorbing heat better than air. Plus, it takes time for the water to travel through the network of pipes and heat your home. That’s why most people prefer hydronic systems when they live in moderate climates or areas with consistent temperatures.
2. Maintenance
Like other closed-loop water heating systems, hydronic systems also need an expansion tank for safety purposes. You must drain these tanks from time to time to maintain efficiency.
3. Higher Installation Costs
Although hydronic systems are versatile and help save costs in the long run, the initial cost of installation is a bit steep. Moreover, installing hydronic systems into a ready-made home is a hassle, and you must hire professional builders to access the floor joists.
Conclusion
As you can see, hydronic systems have their pros and cons, but they are highly popular due to their efficient heating mechanism.
With a network of pipes that run underneath the flooring, hot water is carried through the pipes, and heat from the liquid helps warm the surface. Moreover, the surface temperature warms objects in the room and creates a comfortable setting.
Best of all is that you can create separate temperature zones within individual rooms and around the house, which makes hydronic heating systems highly convenient. If you don’t mind the upfront costs, the efficiency, affordability, and low maintenance of these systems ensure they are a valuable investment.



