Earth Houses: Sustainable Design and Environmental Impact
Earth houses represent an innovative approach to sustainable architecture, blending eco-friendly design with harmony with nature. This article explores the concept of earth houses, their historical development, design philosophy, notable projects such as the Lättenstrasse complex in Switzerland, and their influence on sustainable architecture. It also covers the materials used, environmental benefits, and answers common questions about this building style.
History and Evolution of Earth Houses
Earth houses emerged in the 20th century as interest in environmental sustainability grew. In the 1970s, architects in Switzerland and other parts of Europe began experimenting with designs that reduced energy use and leveraged natural resources. These efforts led to homes built partially underground or covered with earth, offering natural insulation and minimizing environmental impact.
Modern earth houses use techniques like sprayed concrete, which allows for strong, curved structures. By the 1980s, earth houses became a symbol of eco-friendly architecture, particularly in Switzerland, where several successful projects demonstrated their potential.


Design Philosophy of Earth Houses
Earth houses aim to blend seamlessly with their surroundings. Their curved shapes, free of sharp angles, reflect natural forms and create a visually appealing connection with the environment. A layer of soil or grass covers the exterior, providing multiple benefits:
- Thermal Insulation: The earth layer retains heat in winter and keeps interiors cool in summer.
- Visual Harmony: The design makes homes appear as part of the landscape.
- Sustainability: Materials like recycled glass and eco-friendly concrete reduce environmental impact.
Living spaces typically face south to maximize sunlight, while bedrooms are placed on the cooler northern side for comfort.
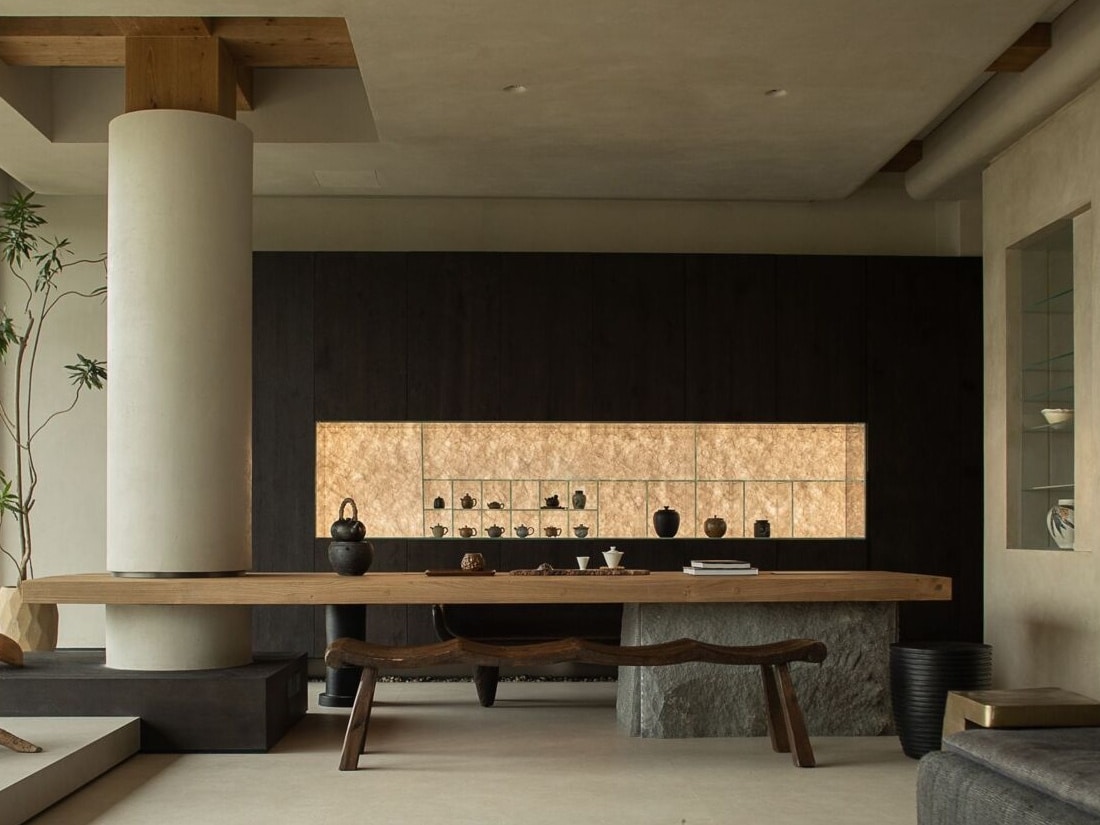
The Lättenstrasse Project in Dietikon
The Lättenstrasse complex in Dietikon, Switzerland, stands out as a prime example of earth houses. It consists of nine homes arranged around a small artificial lake, creating a cohesive living environment. The houses feature curved designs and use insulating materials like recycled glass. Below is a table summarizing key details of the project:

| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Location | Dietikon, Switzerland |
| Number of Houses | 9 houses |
| Materials Used | Sprayed concrete, recycled glass, earth layers |
| Design Orientation | South-facing living areas, north-facing bedrooms |
| Environmental Features | Natural thermal insulation, low energy consumption, integration with nature |
This project shows how architectural design can balance functionality and sustainability, creating spaces that are both practical and eco-conscious.
Source: Scottish Government, 2021. “Sustainable Architecture: Earth Houses.”
Impact on Sustainable Architecture
Earth houses have inspired architectural projects worldwide, serving as a model for eco-friendly construction. Their techniques are applied in residential and commercial buildings, improving energy efficiency and reducing carbon footprints. A report by the World Green Building Council states:
“Sustainable buildings like earth houses can reduce energy consumption by up to 30% compared to conventional structures.”
*Source: World Green Building Council, 2023. “Sustainable Building Report.”
These homes also enhance residents’ quality of life by providing healthy living environments with clean air and natural light.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are earth houses?
Builders construct earth houses using sprayed concrete and cover them with a layer of earth, which provides natural insulation and energy efficiency.
Are earth houses safe to live in?
Yes, they use durable materials like sprayed concrete and include advanced ventilation systems to ensure air quality and safety.
How much does it cost to build an earth house?
Costs vary by location and size, often higher than traditional homes due to specialized techniques, but they save energy costs over time.
Can earth houses be built anywhere?
Yes, in most locations, but soil type, water drainage, and local climate must be considered to ensure sustainability.
Summary Table of Key Points
| Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Concept | Homes covered with earth for insulation and integration with nature |
| Materials | Sprayed concrete, recycled glass, eco-friendly insulating materials |
| Notable Project | Lättenstrasse: 9 homes around an artificial lake in Dietikon, Switzerland |
| Benefits | Up to 30% energy savings, improved quality of life, environmental sustainability |
| Global Impact | Inspiration for sustainable architectural projects worldwide |
Earth houses demonstrate how thoughtful design can protect the environment while improving living conditions, making them a valuable model for future construction.
Earth houses—often built using rammed earth, cob, adobe, or compressed earth blocks (CEBs)—represent one of the oldest yet most sustainable architectural solutions to modern ecological challenges. These homes boast exceptional thermal mass, naturally regulating indoor temperatures by absorbing heat during the day and releasing it at night, reducing energy consumption by up to 60% compared to conventional homes (UN Habitat, 2022). Studies from the University of Cambridge show that rammed earth construction emits up to 70% less CO₂ than concrete. Earth houses also benefit from zero-kilometer materials, as the soil used is often sourced directly from the building site, eliminating transport emissions. In countries like Switzerland, New Zealand, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, earth architecture is regaining attention not just for its ecological advantages but also for its seismic resistance, biophilic aesthetics, and cultural relevance. While durability and moisture resistance remain concerns in humid climates, innovations such as stabilized earth techniques and green roofing systems are making these homes increasingly viable for the 21st century.