Arabic Architecture
Arabic architecture is renowned for its exquisite beauty, intricate designs, and timeless elegance. From the grandeur of mosques to the palaces and fortresses, the wonders of Arabic architecture continue to captivate and inspire. In collaboration with ArchUp, an architecture website dedicated to promoting and showcasing exceptional architectural designs, this article unveils the splendor of Arabic architecture. Join us on this exploration as we delve into the rich history, unique features, and enduring legacy of Arabic architectural design.

Tracing the origins of Arabic architecture
Tracing the origins of Arabic architecture
To truly appreciate the splendor of Arabic architecture, it is essential to understand its roots. Arabic architecture is deeply rooted in Islamic art and culture, with influences from various civilizations that have shaped the region throughout history. From the ancient Egyptians to the Romans and Byzantines, each culture has left its mark on the architectural landscape.
The rise of Islam in the 7th century brought new architectural innovations and a distinct aesthetic to the Arab world. The early mosques, such as the Great Mosque of Mecca and the Al-Masjid an-Nabawi, set the groundwork for the architectural style that would flourish and evolve over the following centuries.
One of the defining features of Arabic architecture is its emphasis on geometric patterns and calligraphy. These intricate designs not only serve as decorative elements but also hold symbolic significance in Islamic culture. From the geometric motifs of Moroccan zellige tiles to the delicate calligraphy adorning the walls of Persian palaces, Arabic architecture is a testament to the mastery of craftsmen and their dedication to creating beauty.
Stay tuned as we continue our exploration in the next section, where we will uncover the unique features that make Arabic architecture truly awe-inspiring.

The defining features of Arabic architecture
Arabic architecture is known for its unique and distinct features that set it apart from other architectural styles. These features not only showcase the craftsmanship and skill of the architects but also hold deep cultural and religious significance.
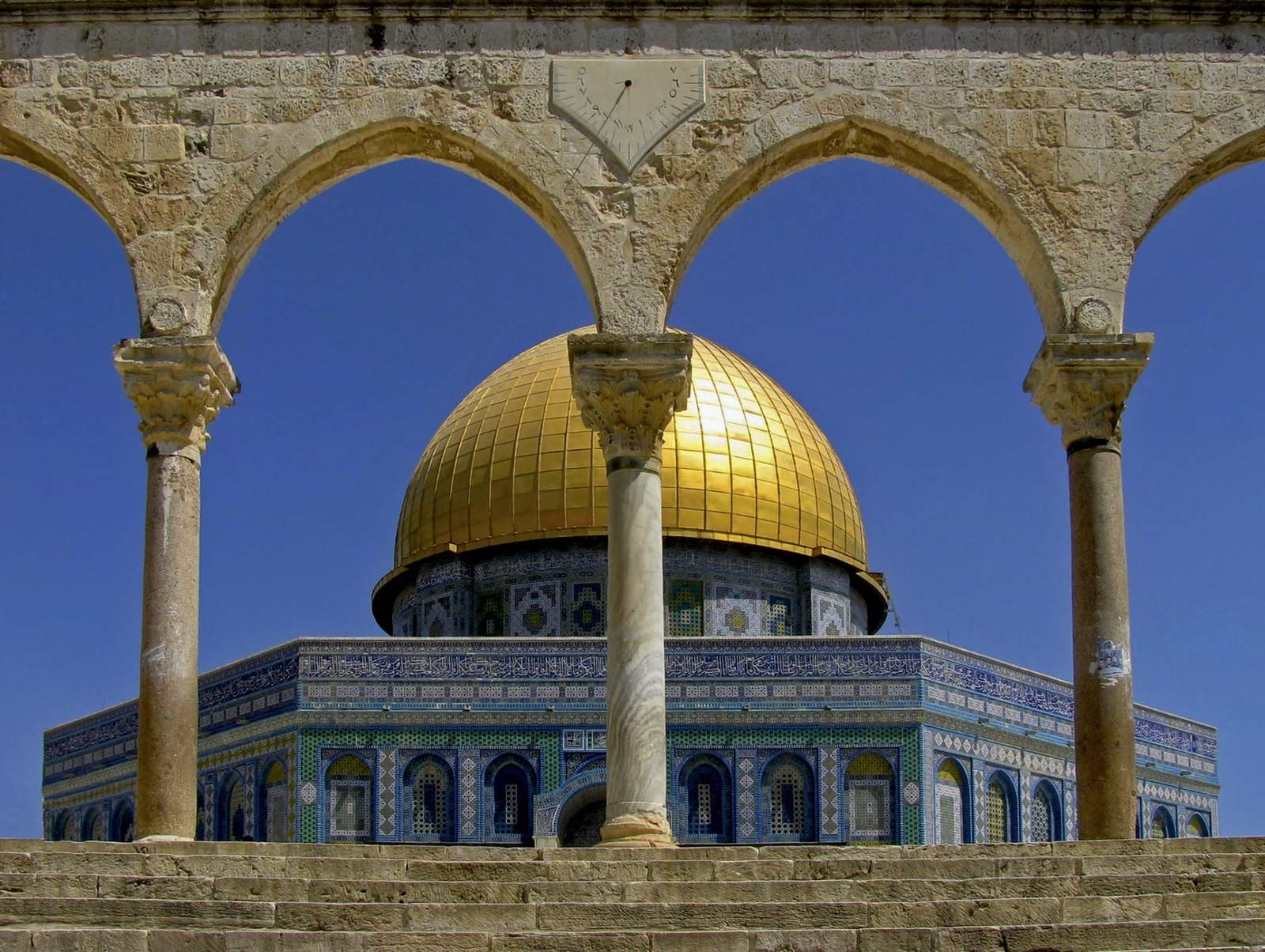
One of the most prominent features of Arabic architecture is the use of architectural elements such as domes and arches. The dome, in particular, is a symbol of the heavens and is often used to cover important spaces such as prayer halls or mausoleums. The arch, on the other hand, is a structural element that adds both elegance and strength to the buildings.
Another characteristic of Arabic architecture is the intricate use of geometric patterns. These patterns can be seen in the design of windows, doors, and even ceilings. The careful arrangement of geometric shapes creates a sense of harmony and order, reflecting the Islamic belief in the divine nature of mathematics and geometry.
Calligraphy is another hallmark of Arabic architecture. The use of Arabic script to decorate walls and surfaces is not only visually striking but also holds great cultural and religious significance. Islamic calligraphy often includes verses from the Quran or quotes from Islamic scholars, serving as a reminder of the devotion and spirituality associated with the buildings.
In addition to these features, Arabic architecture also takes into consideration the environment and climate. Techniques like wind towers, water channels, and courtyards are used to provide natural ventilation and cooling, making the buildings comfortable even in hot desert climates.
Arabic architecture is a testament to the rich history and cultural heritage of the Arab world. Its blend of influences, mastery of craftsmanship, and attention to detail make it truly awe-inspiring. In the next section, we will delve deeper into the different types of Arabic architecture and explore their unique characteristics. Stay tuned for an exploration of the wonders that await!

Iconic examples of Arabic architecture
Now that we have established the distinct features and cultural significance of Arabic architecture, let’s take a closer look at some iconic examples that showcase the splendor of this style.
One of the most famous examples of Arabic architecture is the Great Mosque of Cordoba in Spain. Constructed in the 8th century, this mosque is a remarkable fusion of Islamic and European architectural influences. Its breathtaking interior features a forest of columns, horseshoe arches, and intricate geometric patterns, creating a mesmerizing visual experience.
The Alhambra Palace in Granada, Spain is another gem of Arabic architecture. Built during the Nasrid dynasty, this palatial complex is renowned for its stunning courtyards, elaborate stucco carvings, and exquisite tile work. The Alhambra Palace is a testament to the elegance and opulence that Arabic architecture can achieve.
Moving to the Middle East, the Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque in Abu Dhabi is a modern marvel inspired by traditional Arabic architecture. With its gleaming white marble, vast prayer halls, and grand domes, this mosque reflects the beauty and grandeur of Islamic design, captivating visitors from around the world.
These examples are just a glimpse into the vast wonders of Arabic architecture. In the upcoming section, we will delve into the various regional styles of Arabic architecture, highlighting their unique characteristics and architectural masterpieces. Get ready to embark on an architectural journey like no other!

How Arabic architecture continues to inspire contemporary design
Arabic architecture not only captivates us with its historical grandeur but also continues to influence contemporary design. Its unique blend of intricate geometric patterns, soaring arches, and ornate embellishments has proven to be a timeless source of inspiration for architects and designers around the world.
In modern cities like Dubai and Doha, you can witness the fusion of Arabic architectural elements with contemporary aesthetics. Skyscrapers adorned with intricate facades reminiscent of traditional mashrabiya screens and high-rise buildings featuring beautifully curved and abstract forms pay homage to the rich heritage of Arabic architecture.
Moreover, the emphasis on natural light and spatial harmony found in traditional Arabic buildings has also left an indelible mark on modern architecture. Architects today strive to create spaces that provide a serene and organic experience, drawing inspiration from the courtyards, water features, and shaded balconies of historic buildings.
Arabic architecture’s influence is not limited to the Middle East alone. In cities across the globe, you can find buildings that incorporate elements of Arabic design. From the ornate vaulted ceilings in Andalusian-inspired Spanish homes to the intricate tile work adorning hotels and museums, the splendor of Arabic architecture has transcended borders and cultures.
In the next section, we will explore the regional styles of Arabic architecture in more detail, focusing on their distinct characteristics and iconic structures. Stay tuned to uncover more wonders of this awe-inspiring architectural heritage.
The impact of Arabic architecture on culture and identity
One cannot underestimate the profound impact of Arabic architecture on the culture and identity of the regions it is found in. Buildings and structures are not merely functional spaces but expressions of cultural values, traditions, and beliefs.
The intricate geometric patterns and ornate embellishments found in Arabic architecture are not just visually stunning, but they also hold deeper symbolic meaning. These patterns often represent aspects of Islamic spirituality, such as the infinite nature of God and the balance between order and chaos. Additionally, the use of calligraphy in architectural decoration serves as a reminder of the importance of language and knowledge in Arab culture.
Arabic architecture also plays a crucial role in shaping social interactions and community life. In traditional Arabic dwellings, the central courtyard acts as a gathering place for families and neighbors, fostering social bonds and strengthening community ties. Similarly, the presence of mosques as architectural focal points in cities reinforces the strong role that religion plays in Arab societies.
Furthermore, the incorporation of natural elements, such as water features and shaded courtyards, reflects the importance of nature and the environment in Arab culture. These elements provide a sense of tranquility and harmony, encouraging a connection with the natural world and promoting a sustainable way of life.
In essence, Arabic architecture is not just a physical manifestation of beauty and skill but a living testament to the rich cultural heritage and identity of the Arab world. It is a source of pride, inspiration, and a reminder of the values that have shaped these societies for centuries.
In the next section, we will delve into the historical evolution of Arabic architecture, tracing its roots from ancient times to the present day. Stay tuned as we uncover the fascinating journey of Arabic architectural wonders.

Appreciating the splendor of Arabic architecture
Appreciating the splendor of Arabic architecture is a journey that takes us through time, showcasing the remarkable evolution and innovation that has shaped this unique style. From the grand mosques of the Islamic Golden Age to the intricate palaces and homes of the Arabian Peninsula, Arabic architecture offers a glimpse into the rich cultural history of the Arab world.
One of the most iconic examples of Arabic architecture is the Great Mosque of Cordoba in Spain. Built in the 8th century, it showcases the exquisite blend of Islamic and European architectural influences. The horseshoe arches, intricately carved columns, and stunning mosaics are a testament to the skill and craftsmanship of the architects of that era.
Moving forward in time, we find the stunning Alhambra in Granada, Spain. Built during the 14th century, it is a masterpiece of Islamic architecture with its intricately carved stucco work, serene courtyards, and lush gardens. The Alhambra showcases the perfect harmony between nature and human creativity, a theme that is often found in Arabic architecture.
Another notable example is the Sultan Qaboos Grand Mosque in Oman. Completed in 2001, it blends modern engineering with traditional Islamic design elements. The central dome, adorned with an intricate chandelier and floral motifs, reflects the beauty and grandeur of Islamic architecture.
Arabic architecture continues to evolve today, with contemporary architects incorporating traditional elements into modern structures. The Qatar National Library, for example, combines traditional Islamic calligraphy with modern glass and steel construction, creating a harmonious blend of old and new.
Appreciating the splendor of Arabic architecture is not limited to the structures themselves, but also extends to the experiences and emotions they evoke. It is about standing in awe of the intricate details, feeling the sense of peace in a shaded courtyard, and marveling at the ingenuity of the architects who have left their mark on the world.
Join us in the next section as we explore the key elements and design principles that make Arabic architecture truly captivating and enduring. Stay tuned for a deeper dive into the structural and aesthetic aspects that make these wonders stand tall and proud. You won’t want to miss it!