Complete Guide to CMU (Concrete Masonry Unit) Sizes, Scale, and Specifications
Introduction
In architectural drafting and construction, understanding the dimensions, scaling, and standardization of Concrete Masonry Units (CMUs) is crucial for accurate design, documentation, and execution. This guide presents an in-depth overview of CMU block sizes, scale usage in CAD, and ASTM specification references to help architects, engineers, and builders make informed decisions.
CMU Block Sizes: Nominal vs. Actual Dimensions
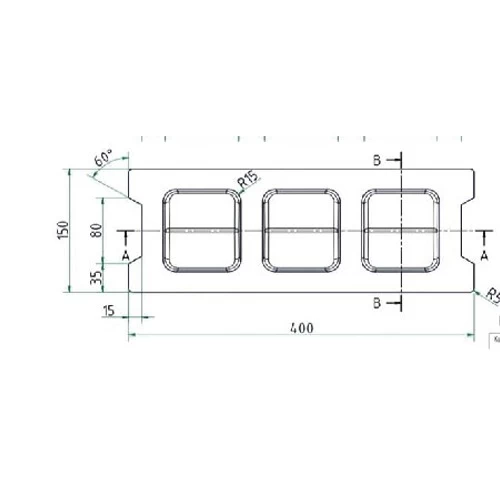
CMU sizes are commonly described in nominal dimensions (which include mortar joints) and actual dimensions (which are the true physical measurements of the unit).
| CMU Size | Nominal Dimensions (D x H x L) | Actual Dimensions (D x H x L) |
|---|---|---|
| 4″ CMU (Full Block) | 4″ x 8″ x 16″ | 3 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” x 15 ⅝” |
| 4″ CMU (Half Block) | 4″ x 8″ x 8″ | 3 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” |
| 6″ CMU (Full Block) | 6″ x 8″ x 16″ | 5 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” x 15 ⅝” |
| 6″ CMU (Half Block) | 6″ x 8″ x 8″ | 5 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” |
| 8″ CMU (Full Block) | 8″ x 8″ x 16″ | 7 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” x 15 ⅝” |
| 8″ CMU (Half Block) | 8″ x 8″ x 8″ | 7 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” |
| 10″ CMU (Full Block) | 10″ x 8″ x 16″ | 9 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” x 15 ⅝” |
| 10″ CMU (Half Block) | 10″ x 8″ x 8″ | 9 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” |
| 12″ CMU (Full Block) | 12″ x 8″ x 16″ | 11 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” x 15 ⅝” |
| 12″ CMU (Half Block) | 12″ x 8″ x 8″ | 11 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” x 7 ⅝” |
Common Uses by Size
- 8″ x 8″ x 16″: Most commonly used for load-bearing and structural walls.
- 12″ x 8″ x 16″: Ideal for retaining or foundation walls.
- 4″ x 8″ x 16″: Used for veneers and non-load-bearing partitions.
Understanding CAD Scale Factors
When working in CAD, all elements are typically drawn at a 1:1 scale in Model Space. Scale factors are applied in Paper Space to correctly print drawings to scale. For example:

| Drawing Scale | Scale Factor |
|---|---|
| 1/32″ = 1′-0″ | 384 |
| 1/16″ = 1′-0″ | 192 |
| 1/8″ = 1′-0″ | 96 |
| 1/4″ = 1′-0″ | 48 |
| 1/2″ = 1′-0″ | 24 |
| 1″ = 1′-0″ | 12 |
Scale factor = Inverse of the drawing scale multiplied by 12 (inches per foot). These factors ensure that objects appear correctly sized on printed sheets.
ASTM Specifications for CMUs
ASTM International sets the standard for concrete block manufacturing to ensure quality and uniformity. Below is a list of relevant ASTM codes:
| ASTM Designation | CMU Type |
|---|---|
| ASTM C55 | Concrete Brick |
| ASTM C73 | Calcium Silicate Face Brick |
| ASTM C90 | Load Bearing Concrete Masonry Units |
| ASTM C139 | Catch Basins and Manhole CMUs |
| ASTM C744 | Prefaced Concrete and Calcium Silicate Units |
| ASTM C936 | Solid Interlocking Concrete Paving Units |
| ASTM C1372 | Segmental Retaining Wall Units |
CMUs must meet these ASTM standards to be approved for construction use. ASTM C90 is the most referenced for conventional building blocks.
Estimated Weight of CMU Blocks by Size
| CMU Type | Nominal Size (inches) | Estimated Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 4″ × 8″ × 16″ Block | Small block | 10–12 kg |
| 6″ × 8″ × 16″ Block | Medium block | 14–18 kg |
| 8″ × 8″ × 16″ Block | Standard block | 18–22 kg |
| 10″ × 8″ × 16″ Block | Heavy block | 24–27 kg |
| 12″ × 8″ × 16″ Block | Extra large block | 28–32 kg |
Factors Affecting CMU Weight by Material Type
| Material Type | Description | Impact on Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Concrete (cement + sand + gravel) | Commonly used in structural and industrial applications | Medium to high weight |
| Lightweight Concrete (e.g., volcanic ash or pumice) | Used for non-load bearing walls or upper floors to reduce dead load | 20–30% lighter than standard |
| High-Density Concrete (with metal or dense aggregates) | Used for radiation shielding or specialty construction | Very heavy (35+ kg per block) |
Weight Variability and Material Impact
It’s essential to note that the weight of a CMU block varies based on the material composition. While traditional concrete blocks made from cement, sand, and gravel provide a standard density suitable for most applications, lightweight alternatives using pumice or volcanic ash can reduce block weight by up to 30%, making them ideal for upper-level construction or thermal insulation.
On the other hand, high-density concrete blocks, often infused with metallic aggregates, can weigh well over 35 kg per unit and are typically used for special cases like radiation shielding or military infrastructure.
Because of this variability, it’s always best to consult manufacturer specifications to confirm the actual weight of CMU blocks, especially when weight plays a critical role in structural design, transportation logistics, or installation methods.
Conclusion
Understanding CMU block dimensions, CAD scaling practices, and manufacturing standards is vital for ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and compliance in architectural and construction projects. Always verify the correct block size and ASTM standard for your application, and consult local building codes or a licensed engineer before beginning work.
Stay tuned to our platform for more technical deep-dives designed for forward-thinking architects and builders.







