Kusatsu Factory Project: Redefining the Relationship Between Industrial Production and the Natural Environment
According to the architectural team’s description, the project presents a model for a new factory dedicated to the production of hair care products and quasi-pharmaceutical items in Kusatsu City, Shiga Prefecture. This project is part of an industrial approach that seeks to integrate aesthetic values with environmental considerations.
Design Vision
The design is based on two central concepts:
1. Beauty as a Core Value
Since its establishment, the manufacturing company has embraced the idea that beauty is not merely a product but an experience created through a series of integrated processes. Therefore, the design aims to reflect this philosophy both visually and functionally.
2. Water as a Source of Life
Given that water is a key element in the production of hair care products, the design emphasizes it as a symbol of sustainability and renewal. Consequently, water becomes both a visual and conceptual element that embodies the project’s spirit.
Harmony with the Environment and Community
In response to the client’s desire to create an eco-friendly factory that does not resemble a conventional industrial building, the architects designed a facility that interacts with its water-rich natural surroundings. Special attention was given to:
- Integrating the building into the local landscape rather than imposing it on the environment.
- Strengthening the relationship between the facility and the surrounding community, making it part of the urban fabric rather than a foreign element within it.


Operational Efficiency through Functional Integration
The project’s design concept focuses on creating a production space that operates more efficiently by integrating functions that were previously distributed across multiple factories into a single facility. Through this integration, it becomes possible to simplify and reorganize the production structure in a more effective way.
To improve the working environment, automated operational systems were implemented to reduce the daily burden on employees and enhance process accuracy. Clear separation between employee movement and material flow also helped establish a streamlined layout that facilitates step-by-step monitoring of the manufacturing stages.
Full Production on a Single Floor
Thanks to this organization, the entire production process can now be executed on a single floor. This includes all essential stages such as:
- Manufacturing
- Filling
- Packaging
- Shipping
This arrangement contributes to minimizing errors, simplifying supervision, and improving responsiveness when adjustments are needed on the production lines.
Certified Quality Standards
To ensure compliance with safety and quality requirements, mixing and filling operations are conducted within cleanrooms that meet ISO 22716 standards for Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in the cosmetics sector. This level of control helps protect the products from any potential contamination.
MES System and Its Role in Enhancing Efficiency
In addition, the factory relies on a Manufacturing Execution System (MES), an information system that manages different production stages in real time. Thanks to the MES, diverse and variable production volumes can be handled more efficiently, making the process more flexible and adaptable to market demands.


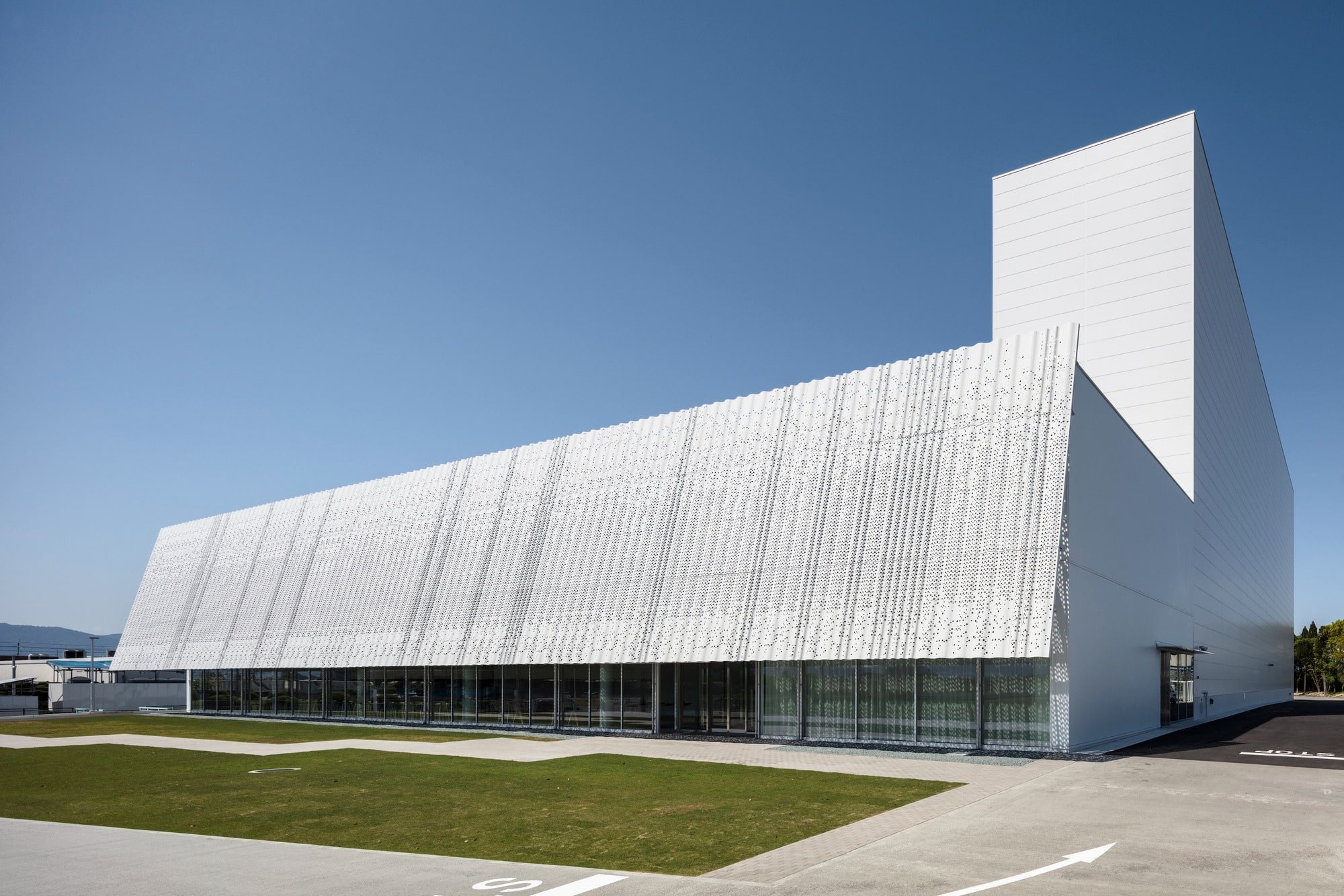
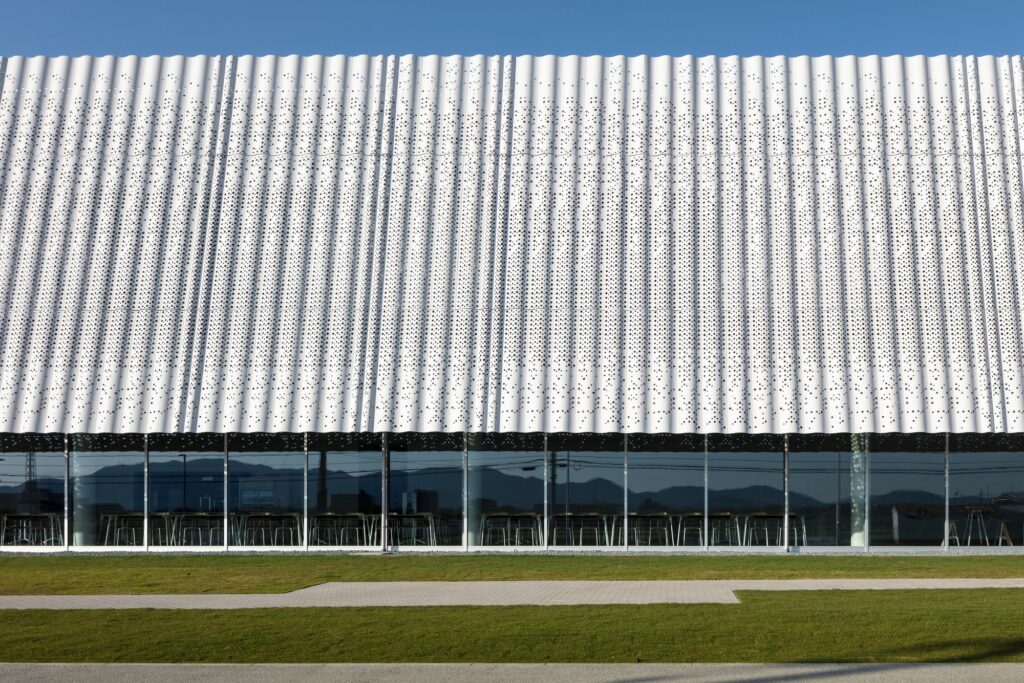
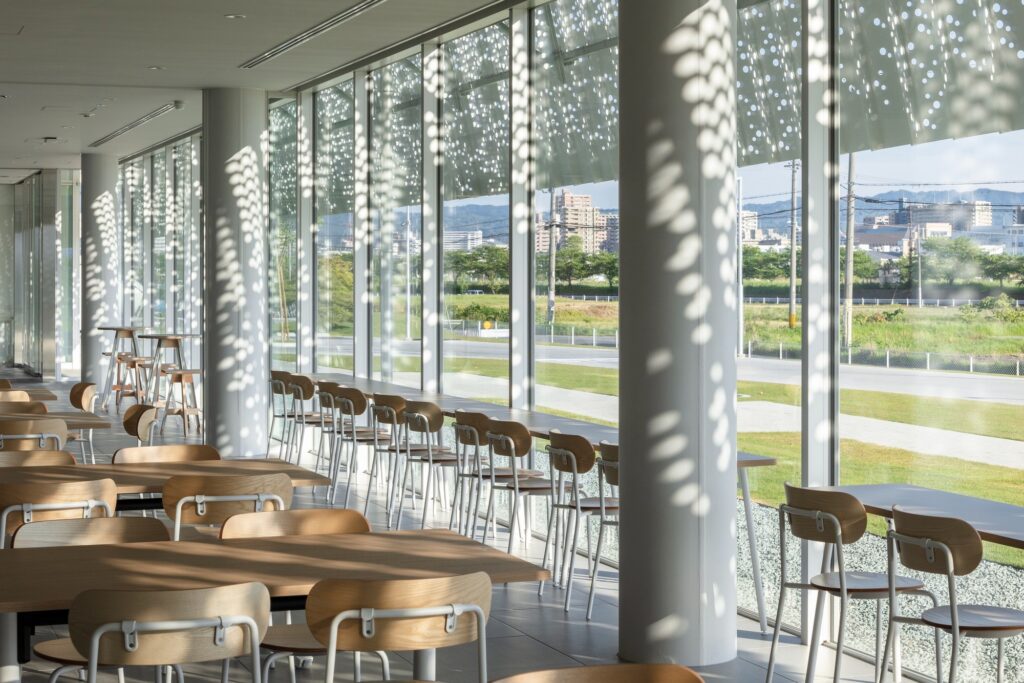
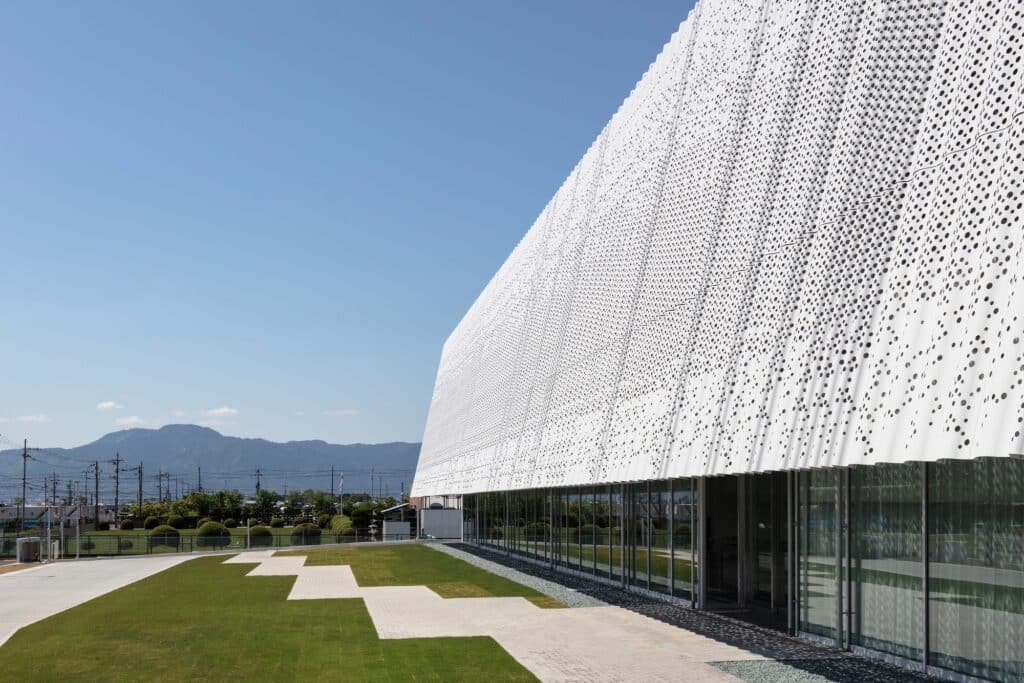
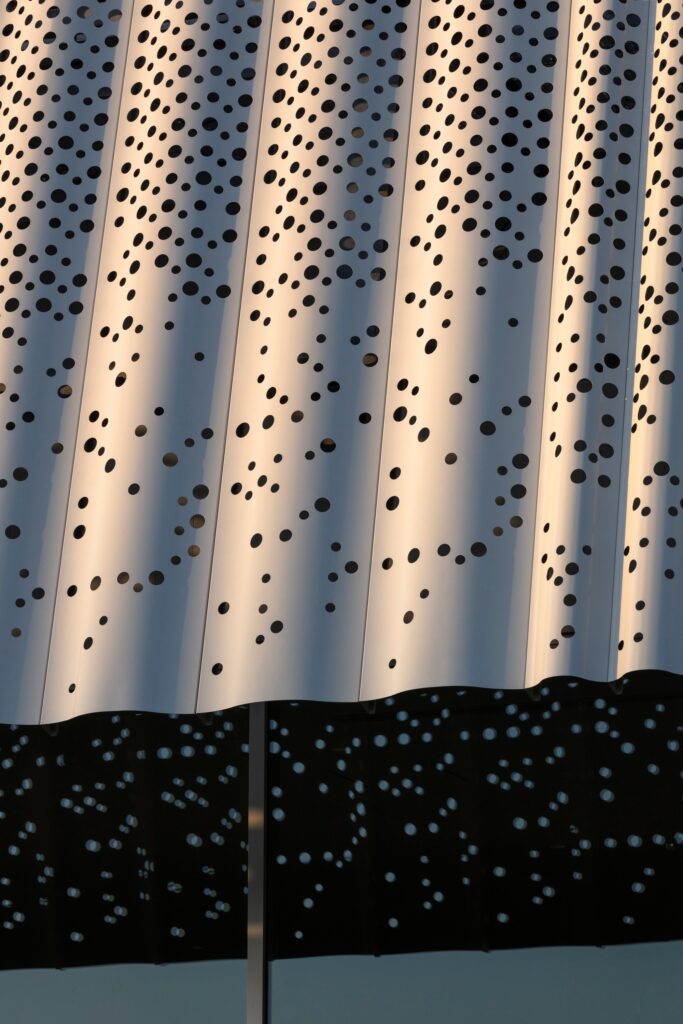
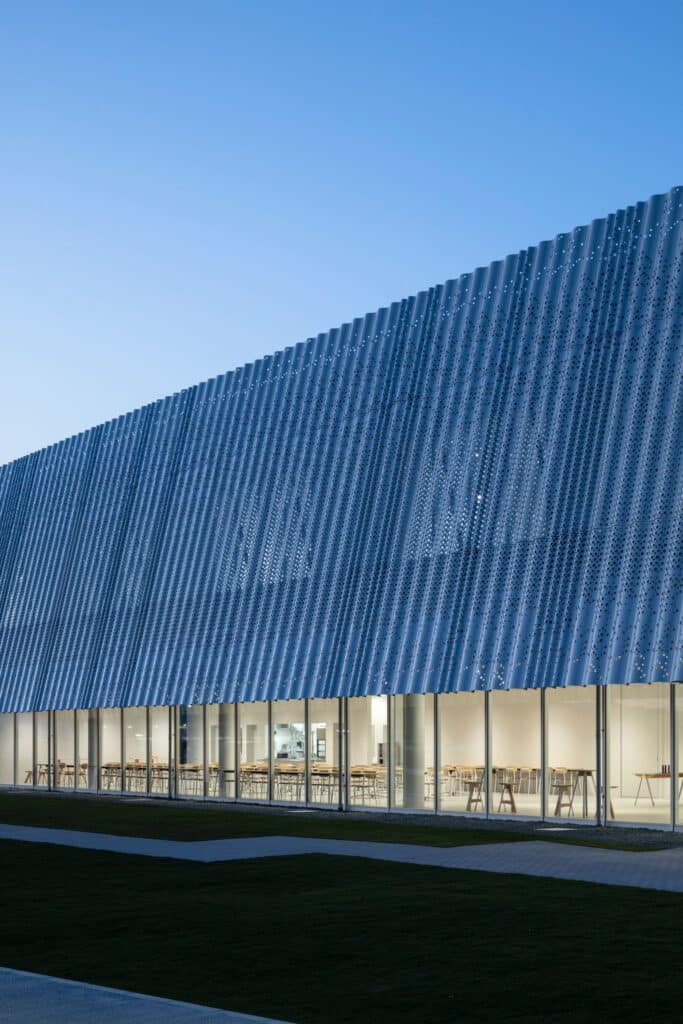
YOSHIZU SKIN as an Environmental Element in the Design
YOSHIZU SKIN emerges as a prominent visual and environmental feature within the project, serving a role that goes beyond traditional aesthetics to become part of the facility’s philosophy of harmonizing with nature. The design of this element is inspired by the reed plant, a natural material long used in the Biwa Lake area of Shiga Prefecture for various purposes since ancient times.
The Function of the Reed Screen and Its Climatic Role
The YOSHIZU barrier, known as the reed screen, is characterized by its air permeability, allowing gentle breezes to pass through. At the same time, it provides protection from direct sunlight, achieving a balance between ventilation and shading without relying on heavy industrial elements.
Light Effects and Transitional Spaces
To enhance harmony, the screen is positioned at a slight angle, giving the impression that it leans against the wall. This orientation, combined with the porous and flexible surface, creates a transitional area where light filters intermittently between the interior and exterior. These visual undulations evoke the shimmer of water on the surface of Lake Biwa, reinforcing the sense of connection with the natural surroundings.
Reducing Heat Load
Practically, this design contributes to lowering the heat load caused by sunlight. The shaded area generated by the reed screen helps reduce the temperature of the façade, supporting the project’s goals of improving building efficiency and using natural solutions to minimize energy consumption.


Efficient Water Management
The project presents an advanced model for managing water resources through an ecosystem specifically designed to minimize water consumption. This is achieved by using treated water for washing dewatering equipment, alongside effective wastewater treatment techniques that support diverse and variable production volumes. These measures help to:
- Prevent water pollution
- Reduce wastewater volume
- Improve energy efficiency in treatment processes
Sustainable Solutions in Energy and Materials
The sustainability strategy also includes:
- Using energy-efficient equipment to reduce environmental impact
- Relying on local raw materials, such as Shigaraki tiles, to support the local economy and reduce emissions from transportation
- Preserving existing trees to enhance harmony with the surrounding environment
Environmental Performance Assessment
As a result of these initiatives, the project received the CASBEE certification with an S rating, a standard that evaluates the environmental performance of buildings. This assessment is the first of its kind in the hair care manufacturing sector, highlighting the design’s commitment to achieving environmental sustainability.

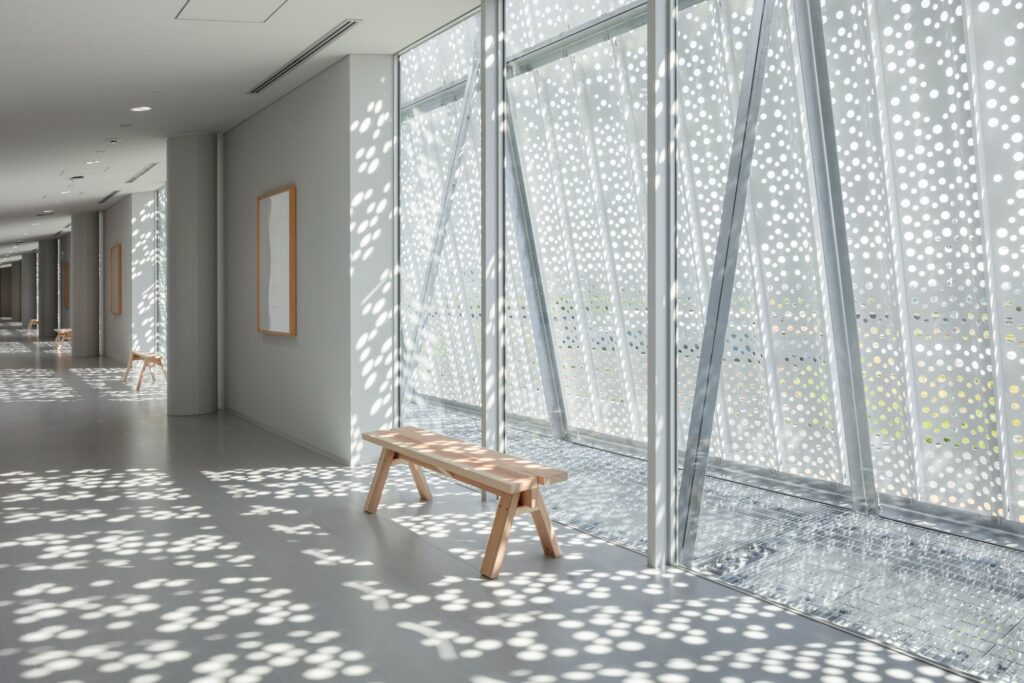
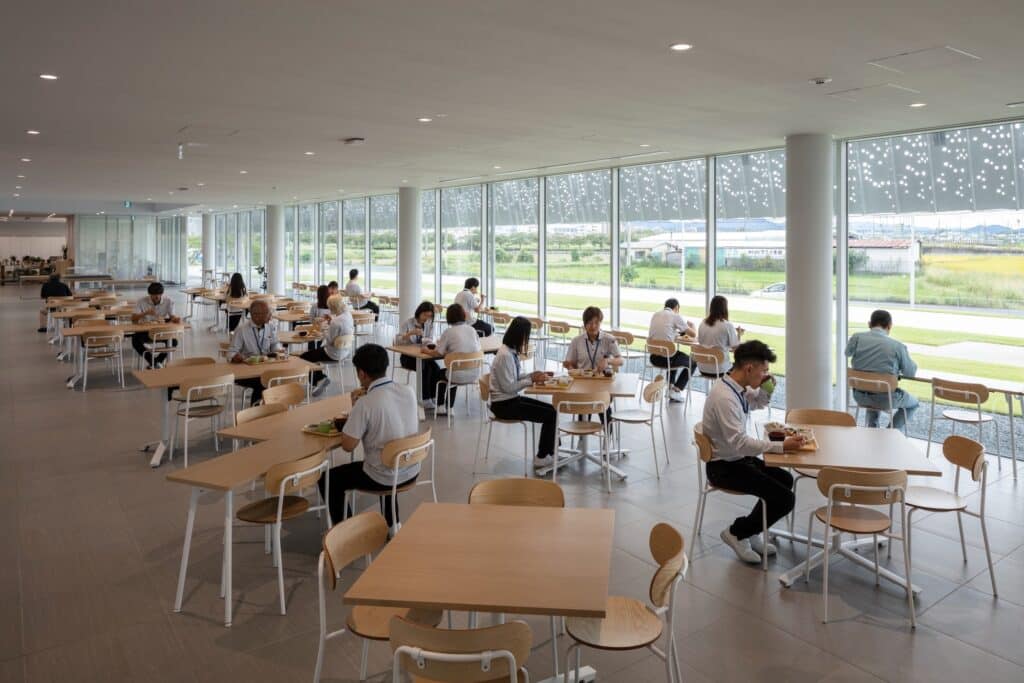
Work Environment and Employee Experience
The design aims to create a comfortable work environment where employees feel proud and a sense of belonging. This was achieved by integrating the reception lounge, equipped with a display area for welcoming visitors, with the dining and break area (cafeteria), which provides a space for relaxation and rejuvenation between work periods.
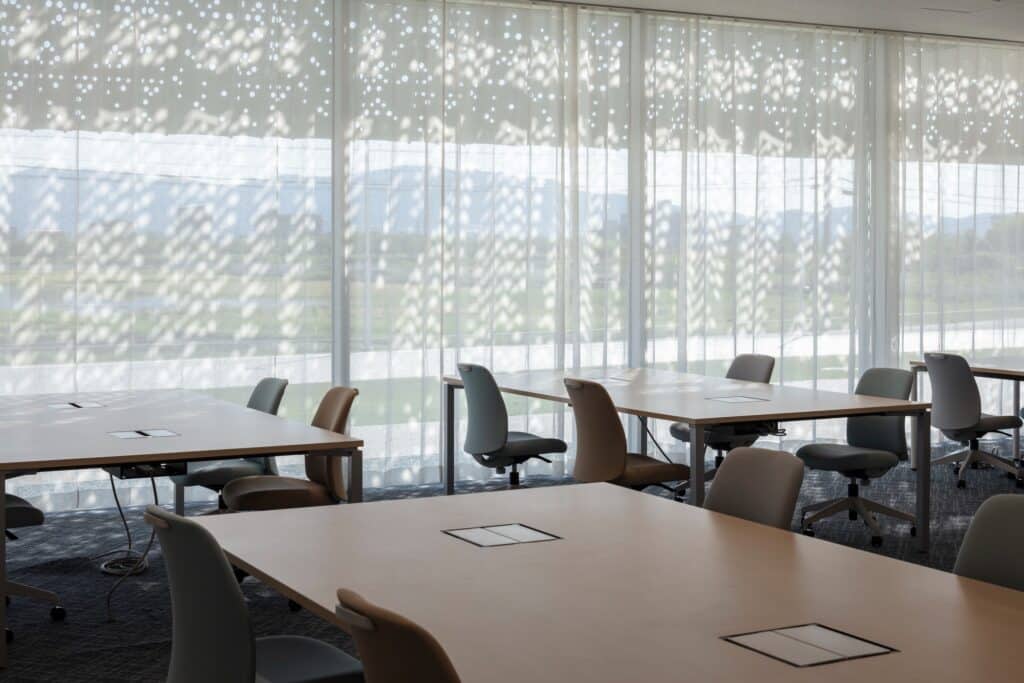
Variety of Seating Spaces
The interior spaces feature diverse seating arrangements:
- Sun-dappled counter seats overlooking the rural landscape, enhancing the sense of connection with nature
- Flexible movable seating, easily repositioned to suit employees’ moods and different needs
This variety allows employees to choose according to the nature of their tasks or how they feel, contributing to improved focus and psychological comfort.
Open Communication Working (OCW) Concept
The project adopted the Open Communication Working (OCW) concept to enhance human interaction and increase production efficiency. The open-plan office facilitates smooth communication among employees of different generations, supporting knowledge and experience sharing.
Moreover, comfort and positive interactions among staff, such as smiles, are regarded as essential elements that contribute to both the aesthetic and functional quality of the workspace.


✦ ArchUp Editorial Insight
The Kusatsu Factory project can be viewed from an architectural perspective as a synthesis of industrial function integration and environmental sustainability, providing an opportunity to observe the evolution of modern factory design approaches. Among its notable strengths, the project demonstrates how design can bridge natural surroundings and production processes, incorporating elements such as the reed screen and water and energy management systems, which offer innovative solutions to minimize environmental impact.
However, the project also raises questions when compared to contemporary industrial architectural standards. For instance, the strong emphasis on environmental and technical integration may limit the flexibility of interior spaces for future expansion or adaptation to changing production needs. Additionally, reliance on automated operational systems and advanced technologies may pose long-term maintenance challenges, requiring continuous resources to ensure their sustainable performance.
On the other hand, the project can be considered an excellent educational model for architects and engineers seeking to explore methods of integrating sustainability into factory design, while highlighting the need to balance environmental performance, functional efficiency, and architectural flexibility. As such, the project remains a rich source of lessons learned rather than a directly replicable model, offering valuable design insights on how to integrate natural elements with industrial production while considering practical constraints over the long term.