Pujiang Platform: Architectural Design Integrating Natural Landscape and Sustainable Visitor Functions
Pujiang Platform: Architectural Integration with Nature
MVRDV has completed the construction of the Pujiang Platform, a unique observation point nestled among the hills south of Chengdu. This project combines its role as a tourist destination with a space for hosting events, taking full advantage of the surrounding natural beauty in central China.
Design Harmonizing with the Natural Surroundings
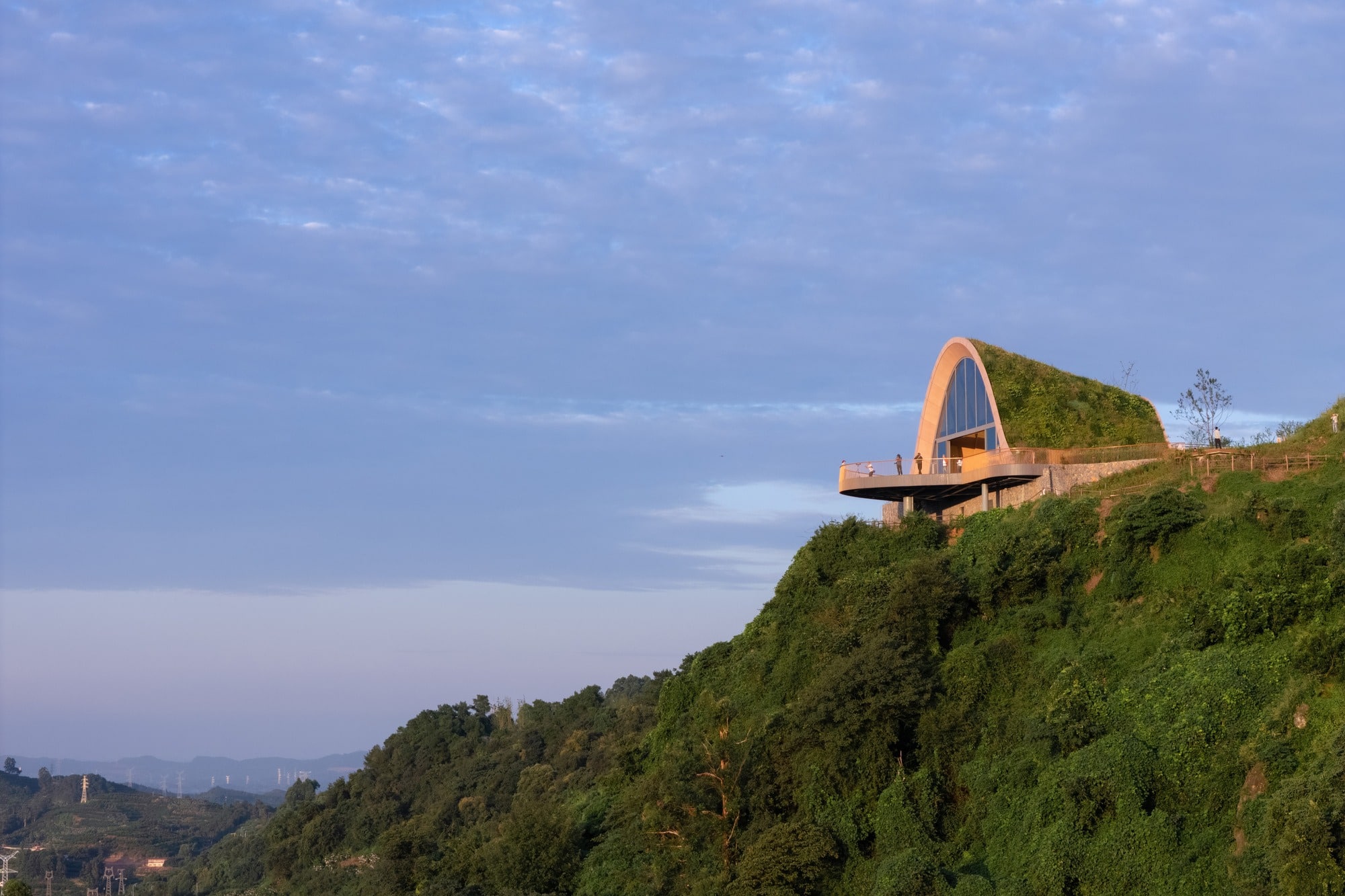
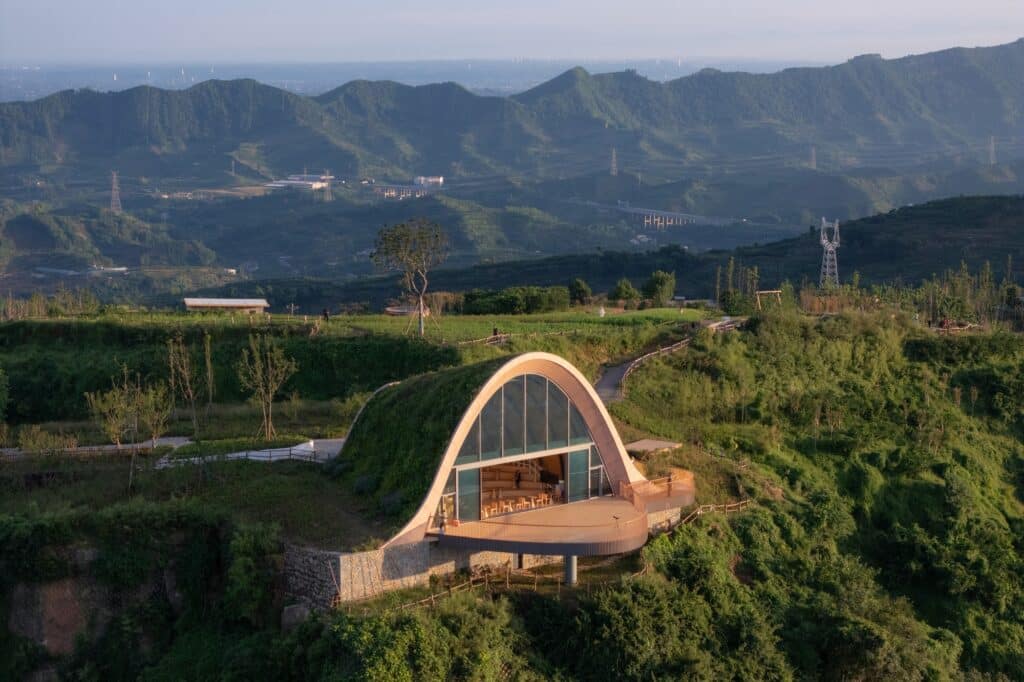
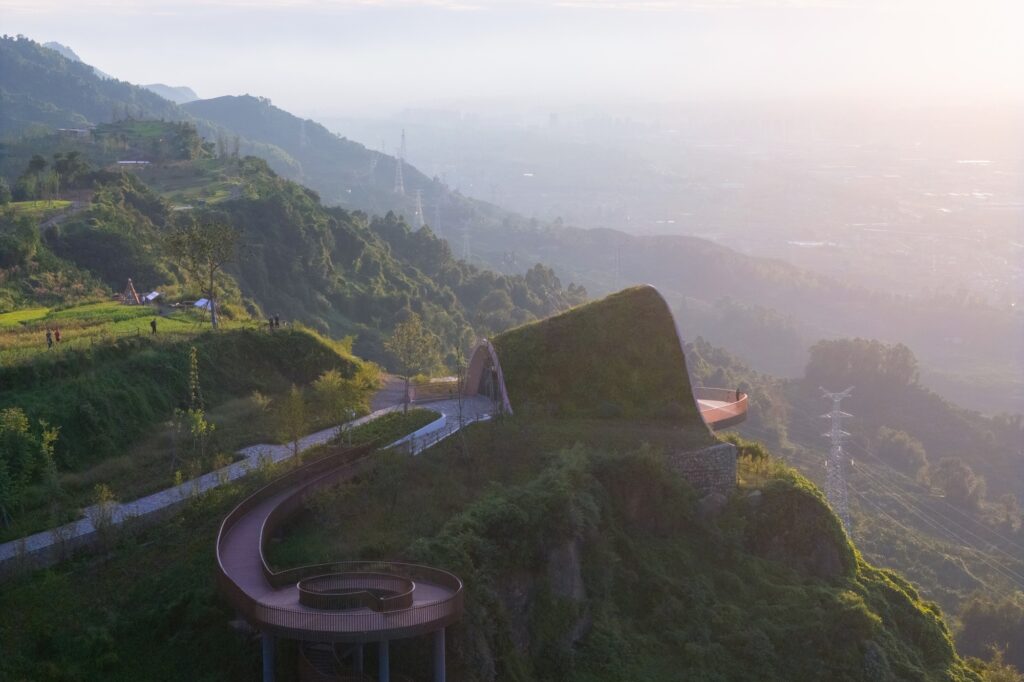
The building is designed to blend seamlessly with the surrounding nature while maintaining its presence as a clear visual landmark visible from the plains below. The structure relies on wooden arches covered with earth, forming a telescopic shape that guides visitors toward a wide observation window and a prominent balcony extending over the slope.
Visual and Functional Experience
This design goes beyond mere visual appeal, creating a holistic experience for visitors. They can enjoy the surrounding landscapes from different heights, while the structure simultaneously provides a functional space for events and activities without impacting the natural environment.


Developing Pujiang City: Towards a Sustainable Lifestyle
The new Pujiang City, located southwest of Chengdu, is currently undergoing development aimed at providing a sustainable and high-quality lifestyle for its residents. The project seeks to integrate urban planning with the surrounding natural environment, reflecting a move toward balanced and sustainable urban growth.
A Strategic Observation Point
In the hills east of Pujiang, there was a simple observation point offering panoramic views of the growing city and the Qionglai Mountain range stretching behind it. This location made the site ideal for transforming it into a distinctive tourist destination where visitors can enjoy and engage with the natural landscapes.
MVRDV’s Role in the Development
MVRDV was commissioned by the Pujiang Planning and Resources Office to develop this point into a multifunctional space. The area can host a variety of events, ranging from weddings to government meetings, while preserving the site’s aesthetic appeal and its connection with the surrounding environment.
Restoring the Hill’s Natural Form
MVRDV’s design began with the understanding that the hill had been flattened during the construction of the previous observation platform. Through an arched wing covered with an earthen berm that blends with the natural landscape, the design aims to restore the hill’s original form, enhancing the sense of integration between the structure and its surrounding nature.
Improving Access Experience
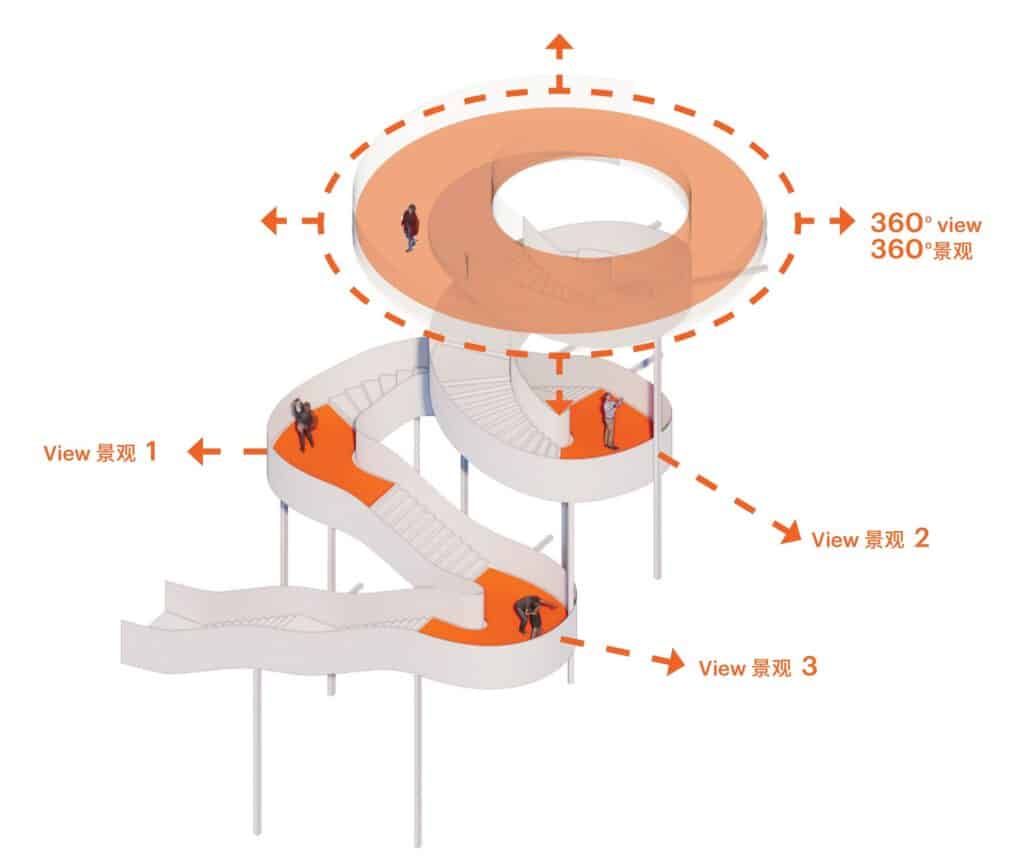
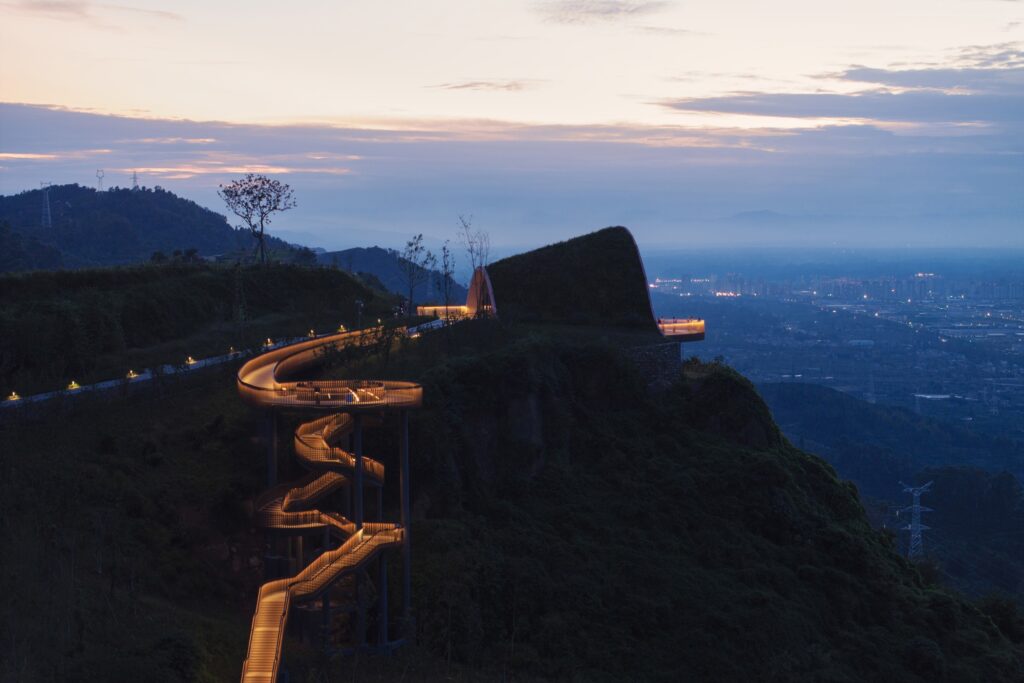
Beyond visual form, the design focuses on enhancing the network of paths leading to the observation point. Several access routes were added, including a secondary viewing platform integrated into a spiral staircase structure, offering visitors diverse options and improving circulation within the site.
Promoting Sustainability Through Wood
The wing was constructed using a wooden framework, serving as a demonstrative model highlighting the potential of wood in Chinese construction. Wood is valued for its ability to reduce carbon emissions compared to traditional materials, although Chinese regulations and the construction industry, in general, remain cautious about its widespread use.

Entering and Experiencing the Interior Space
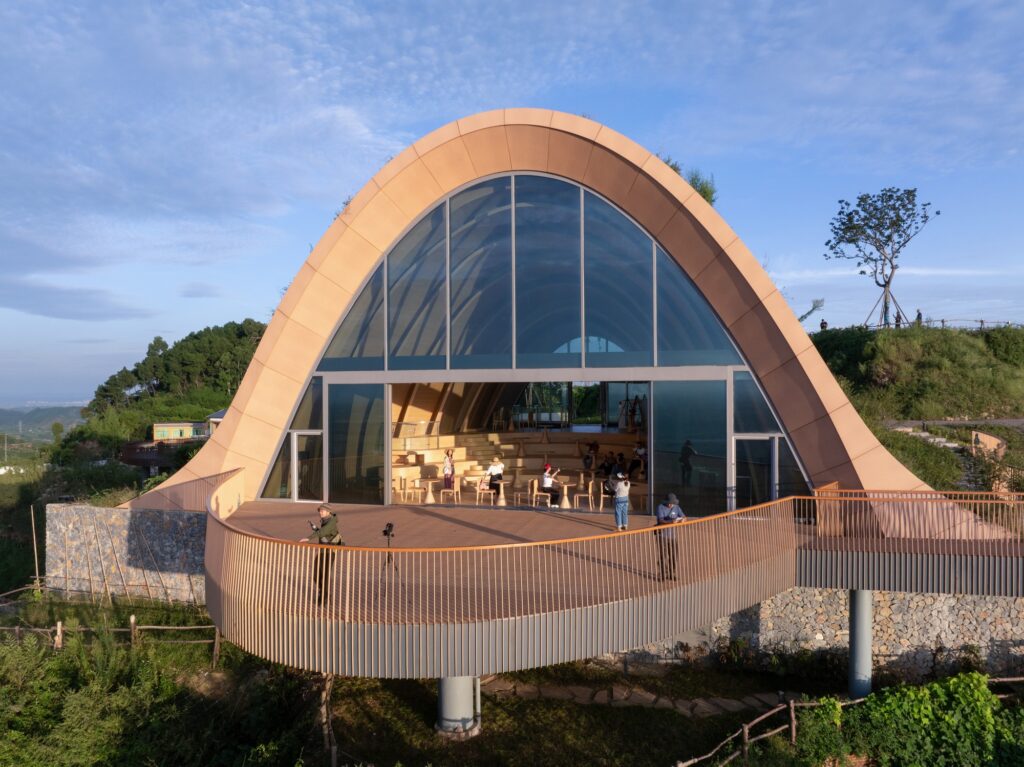
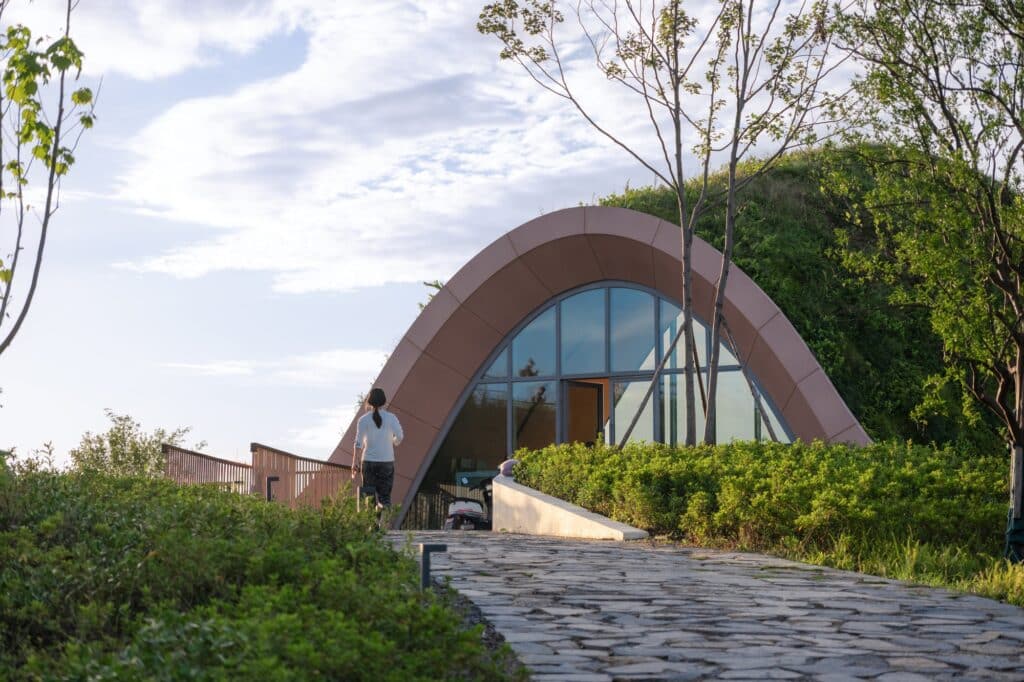
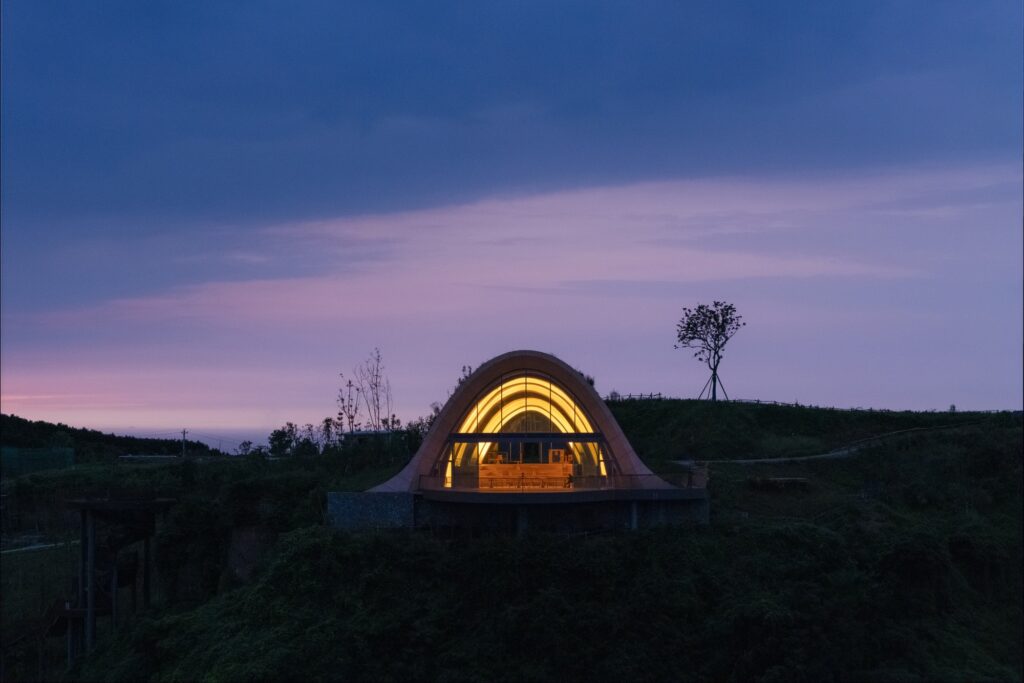
The wing is accessed through a small glass façade integrated into the earthen berm on the building’s southeast side. Upon entering, visitors notice the ceiling gradually rising while the floor level slopes downward, following the natural incline of the hill. This slope creates an ideal tiered area for presentations or for sitting and enjoying the natural scenery through the elevated glass façade, which reaches up to 10 meters.
Enhancing Indoor-Outdoor Connectivity
The façade features a pair of large sliding doors, allowing the interior space to open fully onto the external observation terrace. This feature strengthens both the visual and functional connection between inside and outside, while enabling the terrace to serve as a natural extension of the interior when needed. This enhances flexibility of use and provides a more seamless and enriched viewing experience.
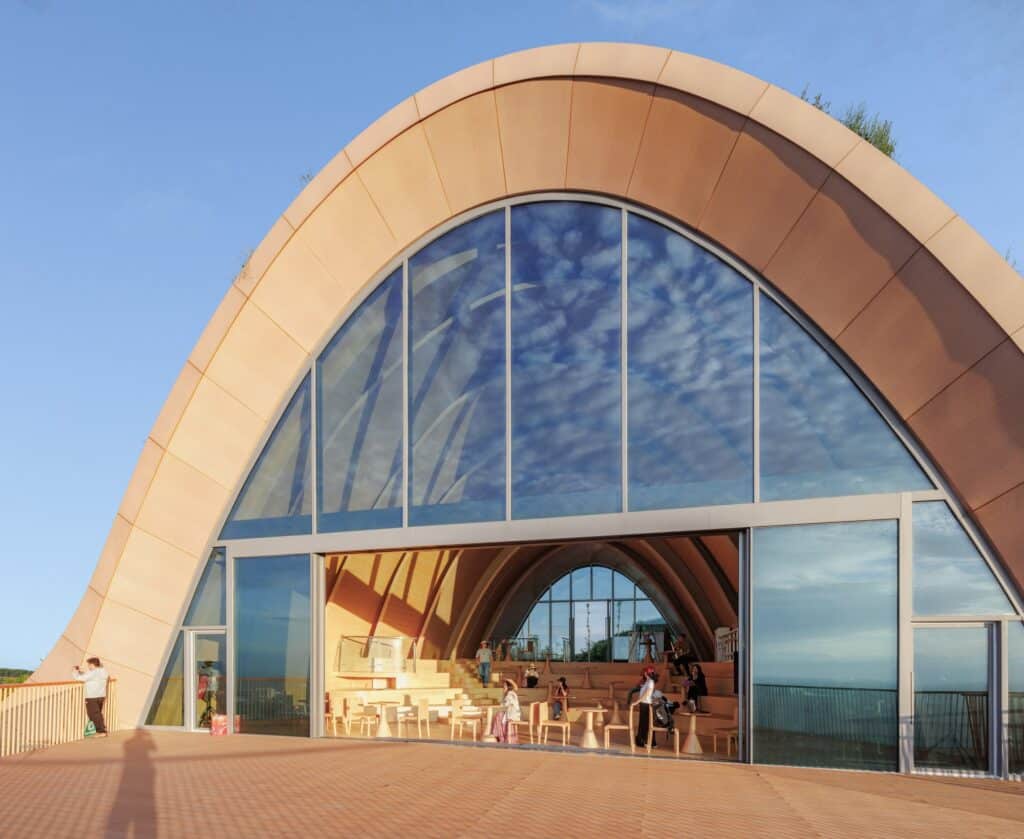

A Design That Respects Nature
Jacob van Rijs, co-founder of MVRDV, notes that the hills in this area represent an exceptional natural landscape, making one of the main challenges maximizing the views while minimizing impact on the surrounding environment.
Reshaping the Hill and Preserving the Environment
He adds: “By adding a hill-shaped wing with a green roof, the goal was not only to reduce the environmental footprint but also to reshape the original hill that existed previously.” This design reflects the essence of a philosophy that preserves and respects nature, which is also evident in the implementation methodology.
Use of Sustainable Materials
The platform relies on bio-based materials such as wood, valued for their high sustainability potential and lower environmental impact on natural sites like this project. This approach demonstrates how architectural beauty can be integrated with environmental responsibility to achieve a balanced and sustainable design.
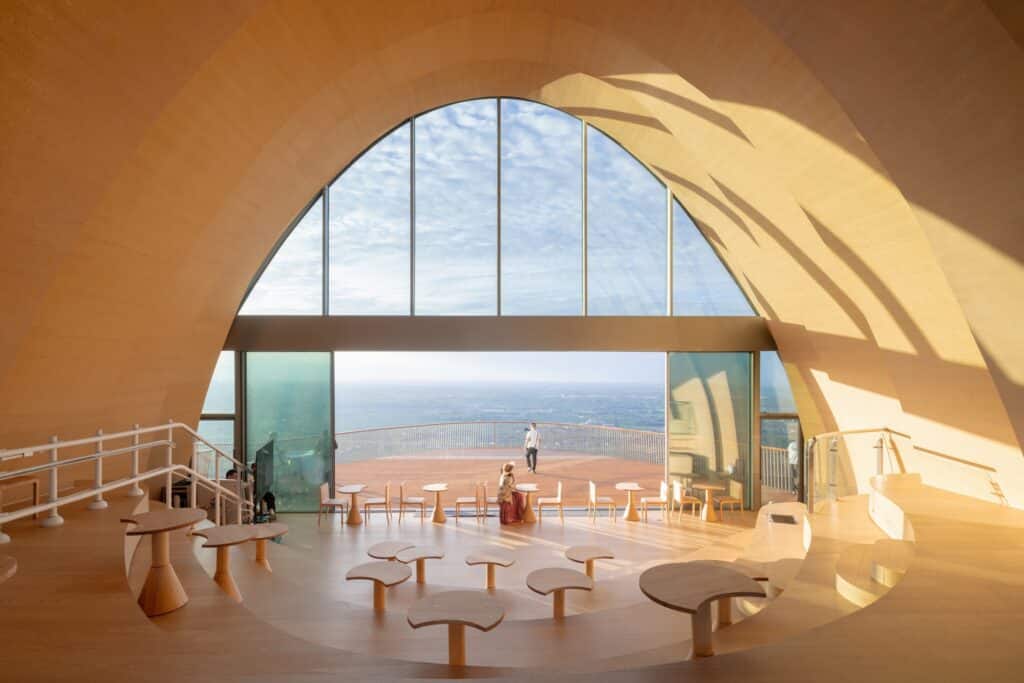

Enhancing Existing Nature
The project’s landscape design aims to enhance the site’s existing elements while focusing on biodiversity. The selected plants reflect this diversity, including the earthen berm over the wing’s roof, which has a soil depth of 10 centimeters, allowing it to host a wide variety of grasses, flowers, and small shrubs.
Sustainable Water Management
Natural watercourses on the site are also utilized to collect rainwater for irrigation purposes. This reflects the project’s commitment to sustainable environmental practices and ensures the longevity of the landscape without relying on external water sources.
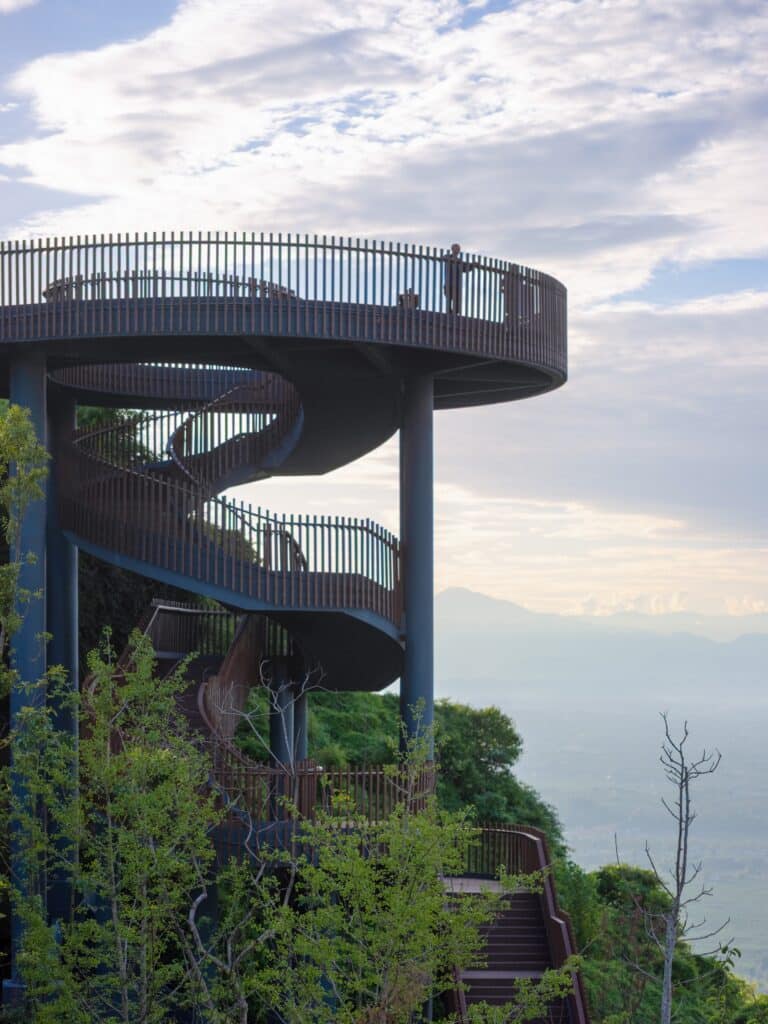

Integrating Pathways and Expanding the Viewing Experience
The design includes the integration of existing site pathways, with the addition of a staircase connecting them to form a continuous circular route. This arrangement provides visitors with a smooth circulation experience while enhancing the opportunity to explore the site progressively and seamlessly.
Secondary 360-Degree Viewing Platform
Above this staircase sits a secondary circular viewing platform, offering 360-degree panoramic views of the distant mountains as well as the nearby natural scenery surrounding the site. This combination of movement and viewing enriches the visitor experience, allowing exploration of the site from different angles, blending interaction with nature and enjoyment of panoramic vistas.
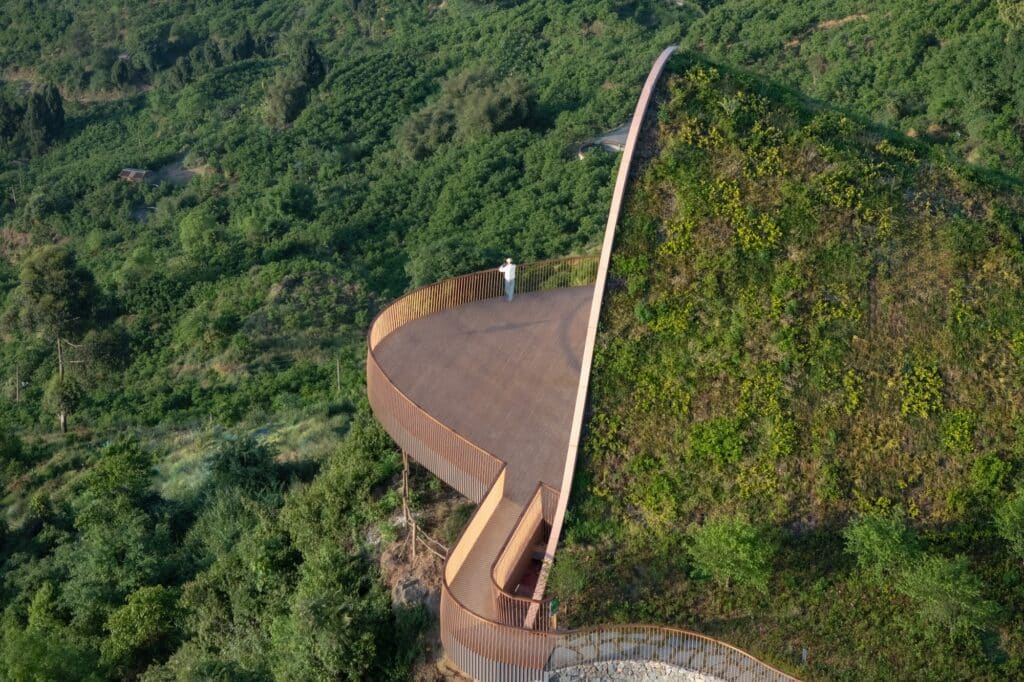


Sustainable Design Strategies
In addition to the wooden structure, which helps reduce embodied carbon emissions, the design incorporates a range of strategies to minimize operational emissions.
Insulation and Thermal Control
The earthen berm and its vegetative cover provide substantial insulation and thermal mass, reducing the impact of temperature fluctuations. The roof is also designed in layers that allow natural ventilation, contributing to sustainable and efficient cooling of the interior space.
Reducing Solar Heat Gain
The large window is oriented toward the north to minimize solar heat gain, while roof overhangs and surrounding trees protect the smaller entrance wall from direct sunlight.
Harnessing Renewable Energy
Furthermore, part of the wing’s energy needs is supplied through a ground-source heat pump, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing reliance on conventional energy sources.

Pujiang Platform as an Example of Sustainability
These features ensure that the Pujiang Platform reflects the identity of the emerging sustainable city at the foot of the hill. It is not merely an observation point but a living model of sustainable architecture that harmoniously integrates with its surrounding environment.
Visitor and Tourist Experience
When visiting the platform, both local residents and tourists can observe how architectural design is integrated with nature in a sustainable and aesthetically pleasing manner.
The Nighttime Beacon
At night, the light emanating from the platform’s windows transforms it into a beacon among the hills, clearly visible from the surrounding plains. This adds a new visual dimension, enhancing the site’s appeal and reinforcing its distinction as a sustainable landmark.

✦ ArchUp Editorial Insight
From an architectural perspective, the Pujiang Platform can be seen as a model that combines sustainability strategies with interaction with the natural environment. The use of wood and the earthen berm represents a tangible step toward reducing the building’s environmental footprint. Additionally, the integration of pathways and the provision of a secondary viewing platform offer visitors a varied experience and reflect a nuanced understanding of movement flow within the site.
However, the project remains limited in its ability to generalize this experience on a larger scale, particularly given challenges related to Chinese regulations and the construction industry’s cautious approach to widespread use of wood. Furthermore, the focus on preserving the natural landscape and hills may make the design less flexible for future uses or adaptation to different architectural styles. In addition, some of the sustainable technologies employed, such as the ground-source heat pump, may require ongoing maintenance and higher operational costs compared to conventional solutions, which could limit their applicability in other projects in the same manner.
Overall, the Pujiang Platform serves as a case study for understanding the balance between architectural design and environmental sustainability, while taking into account the practical and technical constraints that similar projects may encounter. This provides a basis for architectural conclusions that can be discussed in various contexts.
Project information
- Architects: MVRDV
- Area: 414 m²
- Year: 2024
- Photographs:Arch-Exist







