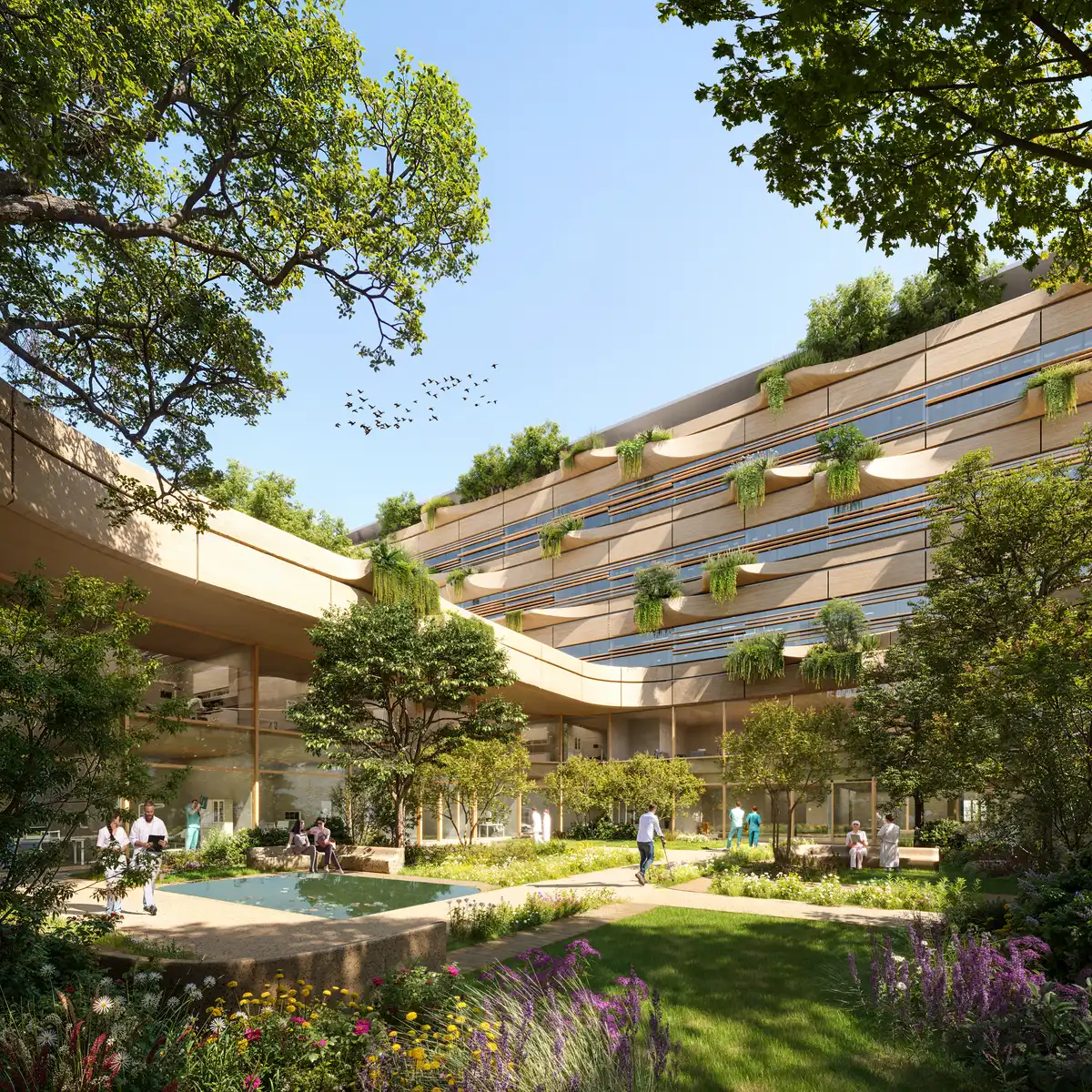
Malpensa Hospital building in Milan by architect Zaha Hadid in the Italian style
The Malpensa Hospital in Milan, Italy, is a major healthcare infrastructure project. Designed after an international design competition, it was awarded to Zaha Hadid Architects . The hospital will merge the Gallarate and Busto Arsizio facilities into one unified campus. Serving nearly one million residents between Milan and Varese, it represents a new approach to medical architecture. This forward looking project integrates advanced care, ecological design, and community access defining 21st century for public health. As a model of responsive planning, Hospital reaffirms the role of architecture in addressing societal needs.
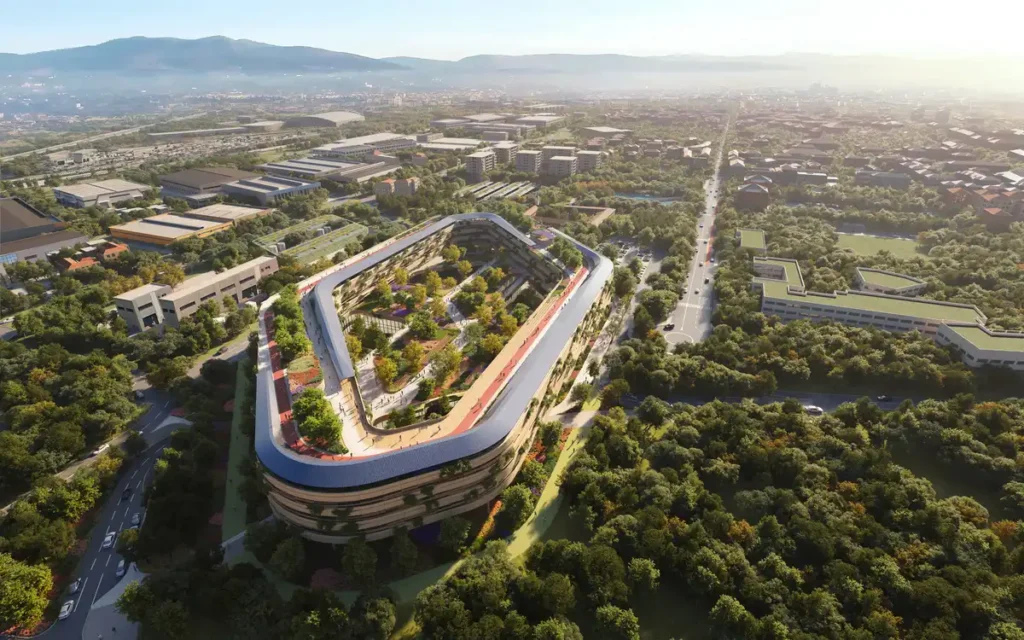

Design Concept
Commissioned by the Lombardy Regional Health Authority, the hospital features five above-ground floors and one basement. It covers approximately 90,000 square meters, organized by care intensity. Emergency, surgery, and critical-care units share a central multifunctional block with radiology and diagnostics. A Main Street at ground level links the entrance plaza to landscaped zones, enhancing public access. Circulation is strictly separated: patients, visitors, staff, and goods each have dedicated routes. This minimizes cross-contamination and supports efficient logistics through an automated delivery system.
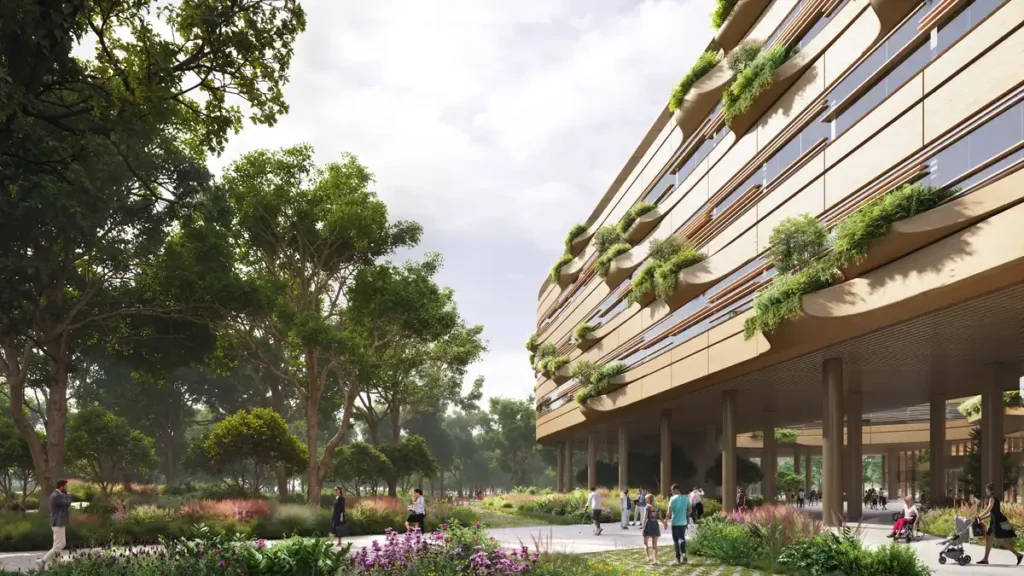

Materials & Construction
Modular prefabrication reduces waste, cost, and construction time. The façade uses aluminum rainscreen panels with integrated planters and solar shading. These were chosen for durability, recyclability, and low embodied carbon. Interior finishes include wood and textiles to promote calm and comfort. All materials meet strict Environmental Product Declaration and Life Cycle Assessment standards. The project exemplifies responsible sourcing in modern building materials.
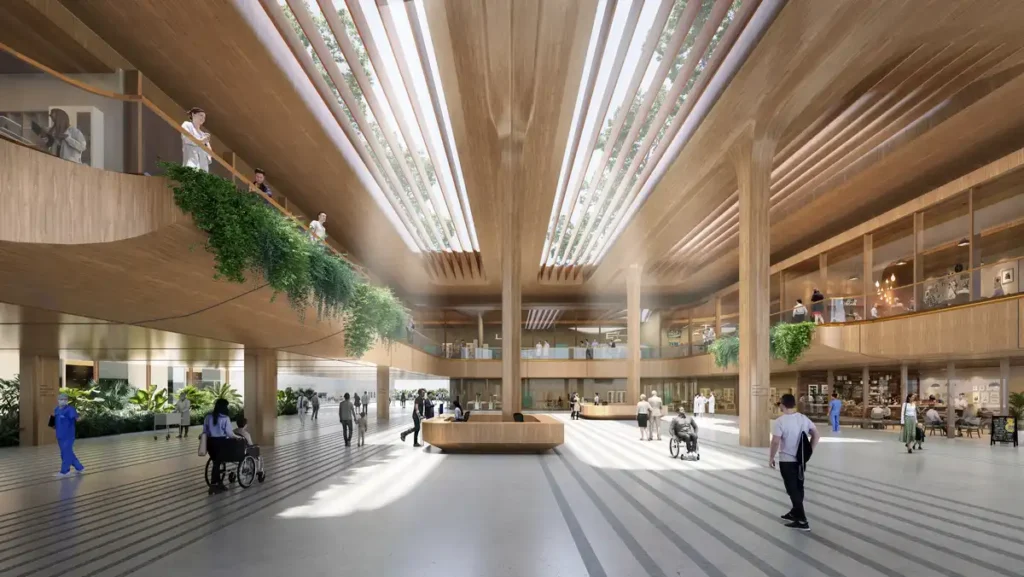

Sustainability
The design exceeds Italy’s CAM environmental standards and targets top-tier certification. A 1 MWp photovoltaic system supplies about 25% of the hospital’s electricity. High performance glazing and solar shading cut cooling demand by 30%. The campus preserves existing woodlands and adds bioswales and wetlands for stormwater reuse. Drought resistant planting reduces irrigation needs. These strategies reflect core principles of sustainability in healthcare infrastructure, informed by ongoing research.
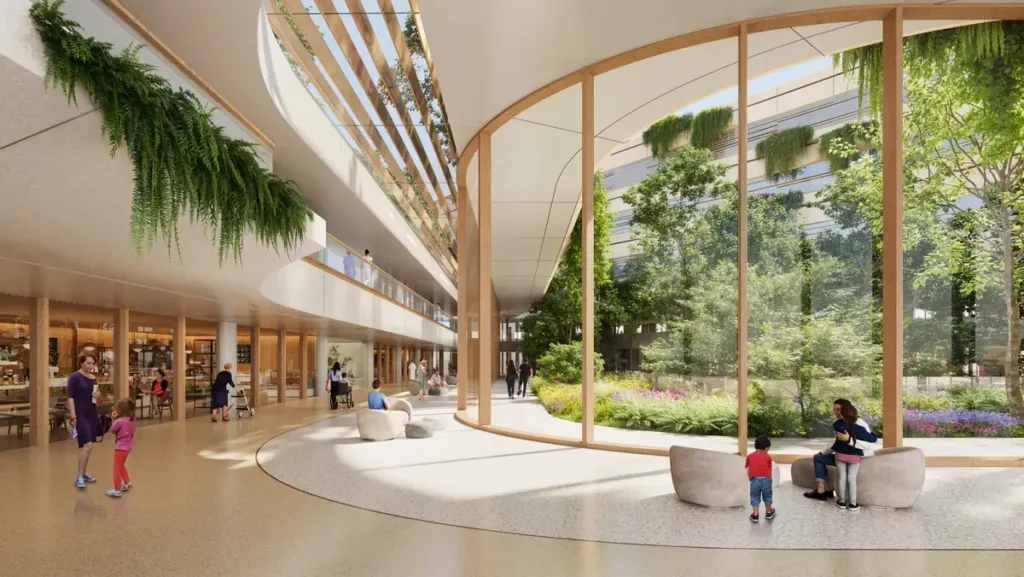

Urban & Community Impact
Located near the Parco Regionale della Valle del Ticino, the site lies within a protected ecological network. The design carefully integrates the historic Cascina dei Poveri, a 12th–13th century rural complex. Public access is reinforced through pedestrian paths, cycling lanes, and transit links from Via Quintino Sella and SS33. Rooftop terraces, courtyards, and gardens support rehabilitation and social interaction. The project rethinks how medical buildings can serve as civic anchors within regional cities. Its human-centered interior design fosters well-being beyond clinical function.
Will this campus inspire similar integrations of healthcare, heritage, and ecology in other regions?
Architectural Snapshot:
Malpensa Hospital in Milan,is a 90,000 sqm modular medical campus integrating advanced healthcare, ecological regeneration, and community-oriented buildings.
ArchUp Editorial Insight
The article delivers a well-structured overview of Malpensa Hospital, drawing exclusively on official statements from Zaha Hadid Architects and avoiding field based critique or deeper inquiry. It adopts an institutional tone and sidesteps critical questions about the design’s socio economic impact or spatial assumptions. It repeats phrases like human centric design as unexamined tropes common in contemporary architecture PR. That said, it records technical and environmental specifications with accuracy, giving it short term archival usefulness. As a contribution to architectural discourse, however, the piece remains locked in the present unlikely to retain relevance or analytical weight beyond its immediate news cycle.